-
斑岩型成矿系统是典型的岩浆热液矿床类型,包括Cu-Au、Cu-Mo、Mo矿床等成矿系列。斑岩型矿床的时空分布、矿床成因与中酸性、发育斑状结构的浅成侵入体具有密切联系(Wu et al., 2021)。黑云母作为斑岩中最常见的暗色矿物之一,属于层状结构硅酸盐矿物,晶体结构为硅氧四面体(T)与八面体(O)以T-O-T方式相间连接构成层状结构,层间阳离子主要为Na+、K+、Li+等,八面体阳离子主要为Mg2+、Fe2+、Al3+等(王汝成等, 2019)。由于黑云母成分对环境改变具有极高的敏感性,因此对其形成时的温压条件、氧逸度等,以及寄主岩石形成时的物化条件、源区性质、构造环境等有良好的指示意义(Wones, 1965; Henry, 2005)。前人通过黑云母矿物化学特征对斑岩型矿床以及与花岗岩有关矿床开展成矿流体演化、岩体含矿性等方面研究(Rasmussen et al., 2013;叶茂等, 2017;蒋华等, 2018)。本文也通过黑云母地球化学组成探讨了其成岩成矿的指示意义。
西南“三江”地区是中国重要的有色金属成矿带之一,Cu、Pb、Zn、Au、Ag等优势矿产资源潜力巨大,格咱岛弧位于“三江”义敦岛弧带南段,该区经历了多次岩浆-构造-热液事件,具有优越的成矿地质条件(邓军等, 2012;李文昌等, 2013a)。红牛-红山铜矿床是区内典型的斑岩-矽卡岩型铜矿床之一,目前红牛、红山2个矿段累计探获资源量超过100 Mt(周云满等, 2020),红牛-红山铜矿床成矿作用与燕山晚期复式岩体密切相关,主要由隐伏的花岗斑岩和石英二长斑岩构成。前人对该矿床成岩成矿事件的时间尺度进行了较好的限定,研究表明矿区内存在两期岩浆活动叠加,分别为晚三叠世和晚白垩世,成矿作用主要发生于晚白垩世(李文昌等, 2011;王新松等, 2011;黄潇肖等, 2012;孟健寅, 2014;彭惠娟, 2014;王鹏, 2016;周杰虎等, 2023)。然而,与复式岩体有关的岩浆作用机制以及导致花岗斑岩、石英二长斑岩含矿差异性的原因尚不清楚。
因此,笔者以红牛-红山铜矿床燕山晚期复式岩体中的黑云母为研究对象,在详细的岩相学基础上,利用电子探针(EMPA)和激光剥蚀等离子体质谱仪(LA-ICP-MS)测试方法,系统测定黑云母的主量、微量元素组成,查明来自2种岩性的黑云母成分差异以及其结晶时的物理化学条件,从矿物学角度为岩石成因类型、成岩成矿作用研究提供理论依据。
1地质概况1.1区域地质背景西南“三江”地区位于中国金沙江、澜沧江、怒江三江并流区域,地处特提斯构造成矿域东部(邓军等, 2020),晚古生代至中生代特提斯洋的多期闭合诱发了一系列大规模构造-岩浆事件,是特提斯-喜马拉雅成矿域的重要组成部分之一(侯增谦等, 2008;李文昌等, 2010)。义敦岛弧位于“三江”造山带东缘,是甘孜-理塘洋壳于晚三叠世向西俯冲形成的近南北向的火山岩浆岛弧(侯增谦等, 2003;李文昌等, 2010;2013b;Deng et al., 2017),北段为昌台弧,南段为格咱弧。义敦岛弧的形成与演化经历了印支期洋壳俯冲、燕山期陆陆碰撞和喜马拉雅期的陆内汇聚3个阶段(杨岳清等, 2002;侯增谦等, 2004),强烈的构造-岩浆-热液活动形成了复杂且独具特色的成矿系统,长期以来吸引了众多中外地质学者的关注。
滇西北格咱地区斑岩-矽卡岩Cu-Mo成矿带位于义敦岛弧带南段,地处中咱地块东缘格咱大断裂以东、甘孜-理塘缝合带以西,向南封闭于扬子陆块西缘(图1a),是义敦-香格里拉Cu-Au-Ag-Pb-Zn多金属成矿带的重要组成部分之一,目前全区累计探获Cu金属量超800万t,Mo金属量50万t,典型矿床包括普朗超大型斑岩型Cu矿,雪鸡坪、红牛-红山、铜厂沟等大中型斑岩-矽卡岩型Cu-Mo多金属矿床(图1b),已成为中国重要的铜钼矿资源基地之一(李文昌等, 2011)。自晚三叠世以来,格咱铜多金属矿集区伴随洋壳俯冲消减形成了印支期斑岩Cu多金属成矿系统(侯增谦等, 2004;李文昌等, 2010;Leng et al., 2014);进入晚白垩世,在碰撞造山作用影响下,该区发生剧烈的碰撞型花岗岩浆侵位事件,形成了斑岩-矽卡岩型Cu-Mo多金属成矿系统(杨岳清等, 2002;邓军等, 2012;刘学龙等, 2016);新生代在青藏高原隆升背景下,形成富碱斑岩Au-Cu为主的多金属成矿系统(李文昌等, 2011;Li et al., 2017)。格咱铜多金属矿集区晚白垩世花岗岩呈近南北向叠加于晚三叠世斑岩成矿带之上,空间上呈现出由北向南依次为出露-半隐伏-隐伏的规律(王承洋等, 2015;Yang et al., 2016;张向飞等, 2022)。
1.2矿床地质特征红牛-红山铜矿床是格咱地区典型的斑岩-矽卡岩型铜多金属矿床,位于格咱铜多金属矿集区中部,属德格-乡城铜铅锌多金属成矿带(侯增谦等, 2004;李文昌等, 2010)。矿区出露地层主要有上三叠统曲嘎寺组三段(T3q3)大理岩、板岩、变质石英砂岩、角砾状灰岩、硅质岩等,曲嘎寺组二段(T3q2)变质石英砂岩、硅质岩、火山碎屑岩、大理岩等。构造较简单,以断裂构造为主,主要呈北西向展布,其次为北东向(图2a)。矿种以铜钼矿为主,局部零星分布金矿、铅锌银矿,含铜矿(化)体总体呈北北西-南南东向平行展布(图2a),空间展布方向基本与矿区地层、主构造线方向一致,矿体形态多为似层状、脉状、透镜状,产出主要受断裂构造和地层控制,主要矿石类型有矽卡岩型、角岩型2种。矿区内发育印支期闪长玢岩、石英闪长玢岩,主要沿红山断裂侵入,形成时代为216~214 Ma(黄肖潇等, 2012);燕山期花岗斑岩-石英二长斑岩复式岩体,主要为隐伏岩体,形成时代为80~76 Ma(周杰虎等, 2023);喜马拉雅期石英闪长玢岩,形成时代为42~40 Ma(刘学龙等, 2022)。前人通过辉钼矿Re-Os同位素年龄限定了矿区成矿年龄为81~77 Ma(徐兴旺等, 2006;王新松等, 2011;Peng et al., 2014),认为矿区成矿主要与燕山晚期造山后伸展作用形成的复式岩体有关(黄肖潇等, 2012),同时也指示了其形成与义敦岛弧晚白垩世岩浆活动存在密切联系(Zu et al., 2016)。
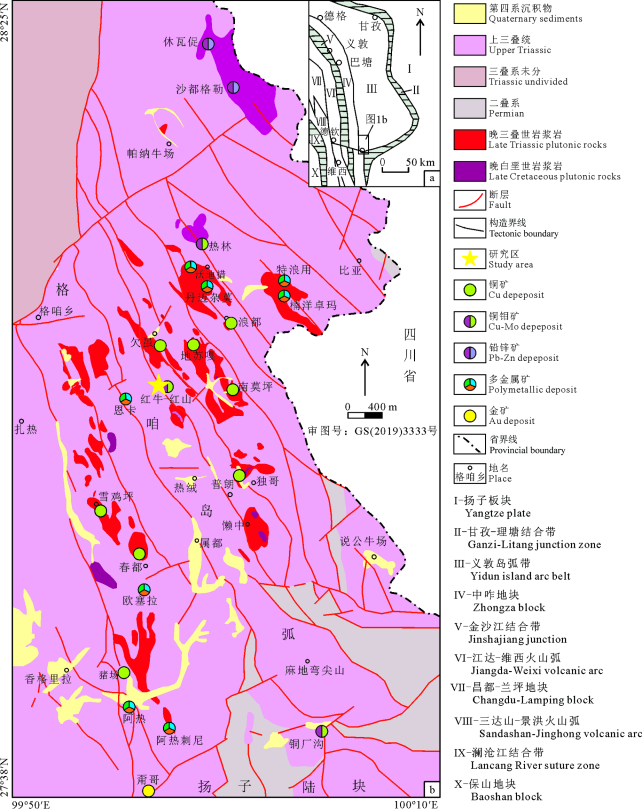
图1滇西北格咱岛弧带构造特征(a)及地质矿产分布图(b,据李文昌等, 2013b;刘学龙等, 2020修改)
Fig. 1 Tectonic features (a) and geological mineral distribution map (b, modified from Li et al., 2013b; Liu et al., 2020) of the Gzan Island Arc Belt in northwestern Yunnan
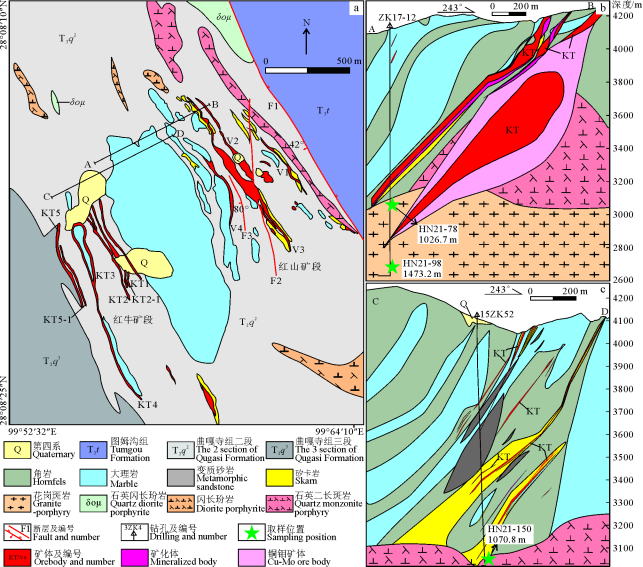
红牛-红山铜矿床中的铜钼矿化与燕山晚期花岗斑岩-石英二长斑岩复式岩体有密切联系,但铜钼在空间上的分布却具有明显的差异性。铜矿化主要以黄铜矿的形式产出,局部可见少量斑铜矿;黄铜矿主要呈浸染状、脉状-细脉状、星点状产于与该复式岩体有关的矽卡岩、角岩中,其次产于斑岩中。钼矿化主要以辉钼矿的形式呈星点状、脉状、细脉状产于该复式岩体中,其次呈星点状产于接触带附近的矽卡岩、角岩中。目前矿区已圈出9条主要矿体群,多呈透镜状、条带状(图2a)。根据已有的钻孔资料,在红山矿段17线深部1000~1500 m范围内揭露出具弱黄铜矿化、辉钼矿化的花岗斑岩(图2b);而在红牛矿段15线深部揭露的石英二长斑岩,发育较强的铜钼矿化(图2c),局部出现全岩矿化。铜钼矿化总体表现出浅部、接触带矿化程度高,向深部逐渐降低的趋势。
图2滇西北红牛-红山铜矿床地质图(a,据周云满等, 2020修改)、17号勘探线剖面图(b)及15号勘探线剖面图(c)
Fig. 2 Geological map of the Hongniu-Hongshan copper deposit (a, modified after Zhou et al., 2020), geological section along No.17 exploration line (b) and No.15 exploration line (c)
2样品特征与分析方法本次研究工作的含黑云母的岩石样品均采自红牛-红山铜矿床深部隐伏花岗斑岩-石英二长斑岩复式岩体中,采样位置如图2b、c所示。黑云母按其产出特征,可分为燕山晚期花岗斑岩中黑云母(类型一),燕山晚期石英二长斑岩中黑云母(类型二)。
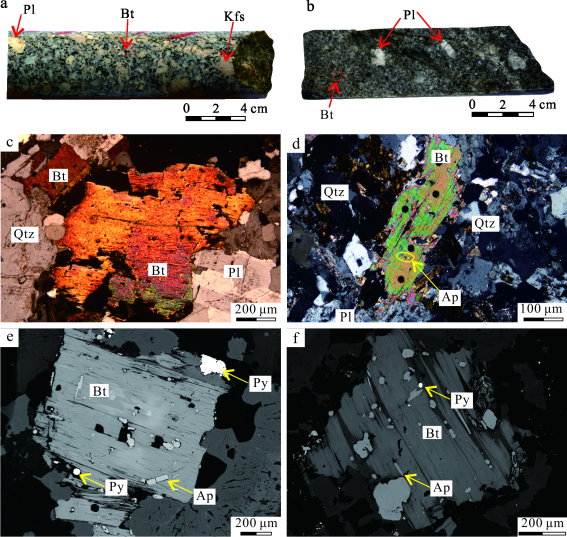
花岗斑岩为隐伏岩体,呈灰白色、浅肉红色,似斑状结构,块状构造。斑晶主要有钾长石、斜长石、黑云母、石英和少量角闪石等,钾长石显示巨晶结构,粒度达1~3 cm(图3a)。副矿物包括磁铁矿、锆石、金红石、磷灰石以及榍石等。手标本中黑云母呈黑褐色,粒径为1~3 mm,含量约5%~10%,在镜下呈自形-半自形鳞片状,多色性明显(浅黄绿~褐色),少数具有裂片、扭曲等特征(图3c)。黑云母总体较新鲜,局部发生了微弱的绿泥石化。黑云母中可见柱状磷灰石,沿黑云母边缘可见黄铁矿颗粒(图3e)。
石英二长斑岩主要为隐伏岩体,地表仅出露小的岩枝,呈浅灰色,斑状结构,块状构造。斑晶主要为斜长石、钾长石、石英、黑云母和角闪石等(图3b),副矿物为榍石、磷灰石等。手标本中黑云母呈深褐色,粒径为1~2 mm,含量约10%,在镜下呈半自形鳞片状,多色性明显(浅黄绿-深褐色),局部发生了绿泥石化(图3d),黑云母中可见针柱状磷灰石及黄铁矿颗粒(图3f)。
黑云母电子探针(EMPA)分析在中国冶金地质总局山东局测试中心完成,采用JEOL公司JXA-8230型电子探针显微分析仪。工作电压15 kV,工作电流20 nA,分析束斑1~2μm。积分时间:主量元素(含量大于1%)的峰值积分时间10~20 s,背景积分时间5~10 s;微量元素(含量小于1%)的峰值积分时间20~40 s,背景积分时间10~20 s。所有数据均采用ZAF法进行基体校正。
黑云母微量元素分析在中国冶金地质总局山东局测试中心利用LA-ICP-MS分析完成。激光剥蚀系统为美国Conherent公司生产的GeoLasPro 193 nm ArF准分子系统,ICP-MS为Thermo Fisher ICAP Q。束斑直径为40μm、频率为6 Hz、能量密度约为10~12 J/cm2。采样方式为单点剥蚀、跳峰采集;采集时间模式为:25 s气体空白+60 s样品剥蚀+25 s冲洗。样品的元素含量计算运用ICPMSDataCal数据处理程序(Liu et al., 2008),采用归一化法(Ca)校正。
3结果分析3.1电子探针分析结果笔者等共测定红牛-红山铜矿床燕山晚期复式岩体中的2类黑云母共56组电子探针数据(包括类型一30组,类型二26组)。电子探针分析结果如表1所示。黑云母阳离子数计算以22个氧原子为基准,采用路远发(2004)提供的Geokit软件计算黑云母的阳离子数及相关参数,并利用林文蔚等(1994)的计算方法获得黑云母的Fe3+和Fe2+值。
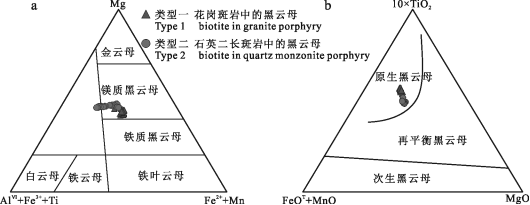
黑云母根据固溶体中Al、Fe、Ti、Mn、Mg元素的相对含量不同可划分4个端员组分,分别为金云母、富铁黑云母、富镁黑云母、铁叶云母(Rieder et al., 1999)。通过Mg-(AlⅥ+Fe3++Ti)-(Fe2++Mn)图解(图4a)对黑云母成因类型进行划分,2种类型黑云母数据点均落于镁质黑云母范围。将所有样品数据点投影于10×TiO2-(FeO+MnO)-MgO图解(图4b)中,显示2种类型黑云母均为原生黑云母(Nachit et al., 2005)。
红牛-红山铜矿床燕山晚期复式岩体中2类黑云母w(SiO2)=36.51%~40.07%,平均37.85%;w(K2O)=4.70%~9.66%,平均8.46%;w(FeOT)=17.49%~19.91%,平均19.13%;w(TiO2)=2.95%~4.18%,平均3.58%;w(Al2O3)=12.55%~13.49%,平均12.91%;w(MgO)=11.01%~13.75%,平均12.40;Mg/(Mg+Fe2+)变化范围为0.58~0.74,平均0.64;整体表现为低Al,高Mg、Ti的特征。样品Fe2+/(Mg+Fe2+)变化范围为0.26~0.42,均值0.36,标准差为0.05,比较均一,指示2类黑云母几乎未遭后期流体改造(Stone, 2000)。此外,2类黑云母CaO含量极低或未能检出,指示其基本未受后期热液流体蚀变作用的影响(绿泥石化、碳酸盐化等),表明红牛-红山燕山晚期复式岩体中2类黑云母产生于原生岩浆结晶作用(Kumar et al., 2010),同时也表明本次测试的黑云母均为岩浆成因。
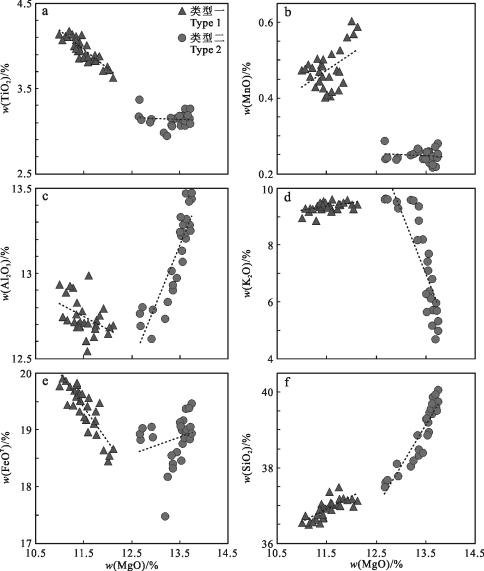
2类黑云母XMg值分别为:类型一(0.50~0.54,均值0.51),类型二(0.54~0.57,均值0.56),其中类型二具有更高的XMg值。主量元素特征显示,石英二长斑岩中的黑云母(类型二)较花岗斑岩(类型一)具有更高的w(MgO)。如图5a~f所示,类型一黑云母中w(TiO2)随w(MgO)升高而降低,降低速率明显高于类型二;类型二w(Al2O3)随w(MgO)升高迅速上升,相反类型一则呈现缓慢降低趋势;类型二w(K2O)随w(MgO)升高急剧降低,类型一则缓慢升高;类型一黑云母w(FeOT)随w(MgO)升高而降低,类型二则与之相反;2种类型黑云母中w(SiO2)与w(MgO)均呈明显正相关关系。
3.2黑云母LA-ICP-MS成分分析在岩相学和EMPA研究的基础上,笔者测定了红牛-红山铜矿复式岩体中2种类型黑云母共22组LA-ICP-MS数据(类型一11组,类型二11组,数据见表2)。
图3红牛-红山铜矿床花岗斑岩、石英二长斑岩手标本(a、b)及黑云母显微特征(c~f)照片
a.花岗斑岩手标本;b.石英二长斑岩手标本;c.花岗斑岩中呈扭曲状的半自形鳞片状黑云母(正交偏光);d.石英二长斑岩中半自形鳞片状黑云母(正交偏光);e.花岗斑岩中呈板状分布的黑云母,其中发育柱状磷灰石及黄铁矿颗粒(反射光);f.石英二长斑岩中呈鳞片状分布的黑云母,其中发育针柱状磷灰石及黄铁矿颗粒(反射光)
Bt—黑云母;Qtz—石英;Pl—斜长石;Kfs—钾长石;Ap—磷灰石;Py—黄铁矿
Fig. 3 Hand specimen and microscopic characteristics of granite porphyry, quartz monzonite porphyry (a, b) and biotite (c~f) in Hongniu-Hongshan copper deposit
a. Granite porphyry hand specimen; b. Quartz monzonite porphyry hand specimen; c. Distorted semi-automorphic scaly biotite in granite porphyry (orthogonal polarization); d. Semi-automorphic scaly biotite in quartz monzonite porphyry (orthogonal polarization); e. Biotite in the shape of plate in granite porphyry, in which columnar apatite and pyrite particles are developed (reflected light); f. Scaly distribution of biotite in quartz monzonite porphyry, in which needle columnar apatite and pyrite particles are developed (reflected light)Bt—Biotite; Qtz—Quartz; Pl—Plageoclase; Kfs—K-feldspar; Ap—Apatite; Py—Pyrite
图4红牛-红山铜矿床黑云母成分图解
a. Mg-(AlⅥ+Fe3++Ti)-(Fe2++Mn)分类图(据Foster, 1960);b. 10×TiO2-(FeOT+MnO)-MgO类型图(据Nachit et al., 2005)
Fig. 4 Chemical composotional diagram of biotite from the Hongniu-Hongshan copper deposit a. Mg-(AlⅥ+Fe3++Ti)-(Fe2++Mn) classification diagram (after Foster, 1960); b. 10×TiO2-(FeOT+MnO)-MgO classification diagram(after Nachit et al., 2005)
本次测试的所有黑云母稀土元素含量均较低,很多元素含量位于检测限之下。稀土元素总量(ΣREE)分别为类型一0.02×10-6~42.18×10-6,均值4.91×10-6;类型二0.02×10-6~14.98×10-6,均值1.71×10-6。微量元素分析结果显示,黑云母中高于检测限的元素主要有Rb、Ba、Sr、Pb、Ga、Nb、Li、Sc、V、Cr、Co、Ni、Zn等。
花岗斑岩中的黑云母(类型一)微量元素含量分别为:w(Pb)=0.66×10-6~1.63×10-6,平均1.07×10-6,w(Cu)=0.07×10-6~0.80×10-6,平均0.45×10-6,w(Zn)=227.18×10-6~507.26×10-6,平均292.91×10-6,w(W)=0.32×10-6~1.22×10-6,平均0.82×10-6;石英二长斑岩中的黑云母(类型二)微量元素含量分别为:w(Pb)=0.73×10-6~2.71×10-6,平均1.41×10-6,w(Cu)=0~1.04×10-6,平均0.56×10-6,w(Zn)=340.44×10-6~502.80×10-6,平均395.52×10-6,w(W)=0.05×10-6~2.42×10-6,平均0.53×10-6。其余微量元素含量见表2。
将黑云母主量、微量元素含量与全岩主量、微量元素含量进行平均大陆地壳标准化对比,结果如图6a、b显示。相对全岩组成,类型一黑云母中富集TiO2、FeOT、MnO、MgO、K2O、Rb、Ga、Li、V、Co、Ni、Zn元素,亏损CaO、Na2O、Sr、Pb、Cr元素,说明黑云母是花岗斑岩中TiO2、FeOT、MnO、MgO、K2O、Rb、Ga、Li、V、Co、Ni、Zn元素的主要载体之一;类型二黑云母中富集TiO2、FeOT、MnO、MgO、K2O、Rb、Ga、Li、V、Co、Zn元素,亏损CaO、Na2O、Sr、Pb元素,说明黑云母是石英二长斑岩中TiO2、FeOT、MnO、MgO、K2O、Rb、Ga、Li、V、Co、Zn元素的主要载体之一。
4讨论4.1岩浆结晶的温压条件黑云母的地球化学组成能够反映出岩浆结晶时的物理化学条件(肖庆玲等, 2018)。根据黑云母主量元素组成进行相关计算可以得到黑云母形成时的温度、压力以及氧逸度等相关信息。
温度是岩浆形成过程中的重要控制因素之一。前人研究表明,黑云母中Ti元素含量对其形成时的温度最为敏感,Henry等(2005)基于过铝质泥质变质岩熔融产物中黑云母的Ti元素含量与温度的相关性提出了黑云母的Ti温度计计算公式:
T={[ln(Ti)-a-c (XMg)3]/b}0.333
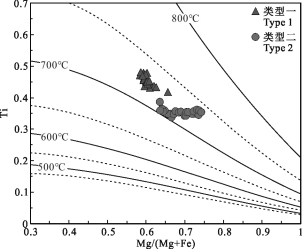
式中T为温度(℃),Ti为以22个氧原子为基准计算的原子数,XMg=Mg/(Mg+Fe),a=-2.3594,b=4.6482×10-9,c=1.7283。公式标定范围:XMg=0.275~1.000,Ti=0.04~0.6 apfu,T=480~800℃。到目前为止,许多学者利用此公式来估算斑岩铜矿床中花岗质岩体结晶温度,例如刘学龙等(2013)利用该公式估算了普朗斑岩型铜矿成矿斑岩体结晶温度为750~800℃;潘彦宁等(2017)估算了滇西北斑岩铜矿带普朗、浪都及松诺矿区含矿石英二长斑岩结晶温度为706~748℃;向坤等(2019)估算了滇西北拉巴地区延燕山晚期斑状花岗岩结晶温度为705~777℃。本文利用此公式对红牛-红山燕山晚期复式岩体中2种类型黑云母进行计算(计算结果见表1),其中,花岗斑岩(类型一)的黑云母Ti温度为737~751℃,平均744℃;石英二长斑岩(类型二)的黑云母Ti温度为722~754℃,平均737℃。在Ti-Mg/(Mg+Fe)图解(图7a)中,2种类型黑云母均位于700~750℃范围之间,与利用公式计算的结果相一致。
图5红牛-红山复式岩体黑云母MgO与TiO2(a)、MnO(b)、Al2O3(c)、K2O(d)、FeOT(e)、SiO2(f)相关图解
Fig. 5 Diagrams of MgO versus TiO2(a), MnO (b), Al2O3(c), K2O (d), FeOT(e) and SiO2(f) of biotite from the Hongniu-Hongshan composite pluton
前人研究表明,黑云母中全铝含量与花岗岩的固结压力具有良好相关性(Uchida et al., 2007),并提出黑云母全铝压力计:
P(×100 MPa)=3.03×AlT-6.53
式中AlT为以22个氧原子基准计算的黑云母中的Al阳离子数,误差为±0.33 MPa。本文利用此公式对红牛-红山铜矿复式岩体中的2类黑云母进行计算,计算结果如表1所示。据压力计算得到类型一黑云母结晶压力为46~72 MPa,平均58 MPa;类型二黑云母结晶压力为37~58 MPa,平均51 MPa。
据公式P=ρgD(ρ=2700 kg/m3,g=9.8 m/s2)计算得出类型一黑云母相应的侵位深度为1.74~2.73 km,平均2.17 km;类型二黑云母相应的侵位深度为1.42~2.20 km,平均1.91 km。
根据鲍文反应序列,黑云母为中酸性岩浆中晚期结晶矿物,黑云母的结晶温度和形成深度用于代表岩浆固结温度和岩体侵位深度,通过对2种类型黑云母温度和压力的计算,红牛-红山燕山晚期复式岩体中花岗斑岩与石英二长斑岩结晶温度分别为744℃和737℃,岩体侵位深度分别为2.17 km和1.91 km,具浅成-超浅成侵位特点。
表1红牛-红山铜矿床燕山晚期复式岩体中黑云母电子探针分析结果(w(B)/%)
Table 1 Electron microprobe analysis data (w(B)/%) of biotite from Late Yanshanian composite pluton in Hongniu-Hongshan copper deposit
组分
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
花岗斑岩(类型一)
SiO2
37.15
37.19
37.16
36.98
36.51
37.05
36.69
36.55
37.04
36.57
36.65
36.75
36.67
36.78
Al2O3
12.70
12.65
12.80
12.69
12.89
12.70
12.71
12.94
12.63
12.73
12.92
12.74
12.69
12.71
TiO2
3.64
3.77
3.72
3.73
4.12
3.95
4.05
4.15
3.84
4.11
4.15
4.08
3.98
4.01
FeOT
18.68
18.45
18.65
18.56
19.87
19.68
19.53
19.78
19.12
19.46
19.44
19.91
19.64
19.71
MnO
0.59
0.60
0.56
0.57
0.49
0.49
0.50
0.47
0.47
0.46
0.43
0.48
0.46
0.50
MgO
12.13
12.02
11.92
12.05
11.15
11.40
11.44
11.01
11.72
11.18
11.29
11.07
11.43
11.33
CaO
0.01
0.02
-
0.01
0.03
0.05
0.03
0.04
0.06
0.02
0.01
0.02
0.02
-
Na2O
0.10
0.10
0.08
0.09
0.14
0.11
0.09
0.11
0.12
0.12
0.12
0.06
0.12
0.06
K2O
9.45
9.46
9.62
9.29
9.21
9.29
9.36
8.97
9.30
9.31
8.87
9.32
9.36
9.40
F
0.90
0.92
0.86
0.86
0.74
0.85
0.91
0.64
0.77
0.74
0.74
0.82
0.78
0.77
Cl
0.14
0.13
0.11
0.14
0.13
0.13
0.14
0.16
0.13
0.14
0.15
0.14
0.14
0.15
总和
95.49
95.31
95.48
94.97
95.28
95.7
95.45
94.82
95.20
94.84
94.77
95.39
95.29
95.42
以22个氧原子为基准计算的阳离子数和相关参数
Si
5.75
5.79
5.78
5.77
5.73
5.77
5.75
5.74
5.78
5.75
5.74
5.76
5.75
5.76
AlⅣ
1.71
1.73
1.75
1.72
1.77
1.72
1.75
1.74
1.72
1.73
1.73
1.72
1.72
1.71
AlⅥ
0.60
0.60
0.60
0.61
0.61
0.61
0.60
0.66
0.60
0.63
0.65
0.64
0.62
0.64
Ti
0.42
0.44
0.43
0.43
0.48
0.46
0.47
0.48
0.45
0.48
0.48
0.47
0.46
0.46
Fe3+
0.89
0.63
0.60
0.67
0.69
0.68
0.66
0.74
0.67
0.67
0.72
0.67
0.69
0.69
Fe2+
1.53
1.77
1.83
1.75
1.91
1.88
1.89
1.86
1.82
1.89
1.83
1.94
1.88
1.89
Mn
0.08
0.08
0.07
0.08
0.06
0.06
0.07
0.06
0.06
0.06
0.06
0.06
0.06
0.07
Mg
2.92
2.90
2.87
2.93
2.73
2.76
2.80
2.71
2.82
2.76
2.78
2.72
2.80
2.78
Ca
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
Na
0.03
0.03
0.02
0.03
0.04
0.03
0.03
0.03
0.04
0.04
0.04
0.02
0.04
0.02
K
1.80
1.82
1.85
1.79
1.78
1.79
1.81
1.74
1.80
1.80
1.72
1.80
1.80
1.80
总和
15.73
15.79
15.80
15.78
15.80
15.77
15.84
15.77
15.77
15.81
15.75
15.80
15.82
15.82
OH*
2.61
2.58
2.65
2.63
2.61
2.58
2.57
2.62
2.62
2.62
2.59
2.62
2.64
2.66
F
0.55
0.54
0.51
0.53
0.46
0.50
0.55
0.43
0.46
0.48
0.48
0.51
0.50
0.50
Cl
0.04
0.03
0.03
0.04
0.04
0.03
0.04
0.04
0.03
0.04
0.04
0.04
0.04
0.04
AlT
2.31
2.32
2.35
2.33
2.38
2.33
2.35
2.39
2.32
2.36
2.39
2.35
2.34
2.35
Fe3+/Fe2+
0.58
0.36
0.32
0.39
0.36
0.36
0.35
0.40
0.37
0.35
0.40
0.35
0.37
0.36
Fe2+/(Mg+Fe2+)
0.34
0.38
0.39
0.37
0.41
0.41
0.40
0.41
0.39
0.41
0.40
0.42
0.40
0.40
XMg
0.66
0.62
0.61
0.63
0.59
0.59
0.60
0.59
0.61
0.59
0.60
0.58
0.60
0.60
Fe#
0.37
0.26
0.25
0.28
0.27
0.27
0.26
0.28
0.27
0.26
0.28
0.26
0.27
0.27
Mg#
0.55
0.55
0.54
0.55
0.51
0.52
0.52
0.51
0.53
0.52
0.52
0.51
0.52
0.52
MF
0.54
0.54
0.53
0.54
0.51
0.51
0.52
0.51
0.52
0.51
0.52
0.50
0.52
0.51
T/℃
747
743
739
744
746
742
746
748
742
748
751
744
744
744
P/MPa
48
50
58
54
69
54
58
72
50
62
70
60
57
58
H/km
1.83
1.91
2.20
2.05
2.61
2.04
2.20
2.73
1.90
2.34
2.65
2.27
2.16
2.18
Ⅳ(F)
0.91
0.91
0.95
0.95
1.00
0.94
0.91
1.06
0.99
1.00
1.00
0.96
0.99
1.00
Ⅳ(Cl)
-4.67
-4.58
-4.48
-4.62
-4.54
-4.54
-4.58
-4.62
-4.54
-4.57
-4.62
-4.55
-4.57
-4.58
Ⅳ(F/Cl)
5.59
5.49
5.43
5.56
5.54
5.49
5.49
5.68
5.54
5.57
5.62
5.51
5.56
5.57
log(fH2O/fHF)fluid
1.32
1.31
1.35
1.34
1.41
1.35
1.31
1.47
1.39
1.41
1.40
1.37
1.39
1.40
log(fH2O/fHCl)fluid
3.22
3.25
3.33
3.22
3.22
3.23
3.19
3.15
3.25
3.20
3.16
3.20
3.21
3.20
log(fHF/fHCl)fluid
0.70
0.73
0.77
0.68
0.61
0.68
0.68
0.48
0.66
0.59
0.57
0.63
0.62
0.60
续表1-1
Continued Table1-1
组分
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
花岗斑岩(类型一)
SiO2
37.09
36.97
36.94
36.91
37.38
36.91
36.57
36.55
36.78
37.01
37.18
37.06
37.51
37.21
Al2O3
12.55
12.72
12.78
12.83
12.61
12.76
12.93
12.68
12.69
12.73
12.70
12.99
12.68
12.75
TiO2
4.01
3.96
4.14
3.98
3.91
4.13
4.18
4.08
3.86
3.86
3.83
3.82
3.90
3.89
FeOT
19.42
19.52
19.64
19.80
19.18
19.60
19.77
19.84
19.34
18.93
19.34
19.58
19.17
19.49
MnO
0.41
0.43
0.40
0.44
0.46
0.45
0.48
0.47
0.48
0.53
0.47
0.52
0.42
0.44
MgO
11.59
11.44
11.49
11.37
11.56
11.36
11.22
11.37
11.43
11.78
11.77
11.61
11.75
11.85
CaO
-
0.02
0.01
0.01
0.02
-
-
0.01
0.01
0.04
0.01
0.01
0.03
-
Na2O
0.07
0.07
0.08
0.10
0.06
0.09
0.11
0.07
0.09
0.09
0.07
0.07
0.09
0.18
K2O
9.34
9.57
9.52
9.36
9.41
9.43
9.29
9.51
9.43
9.46
9.42
9.64
9.47
9.52
F
0.83
0.81
0.86
0.75
0.87
0.82
0.85
0.77
0.72
0.85
0.82
0.79
0.75
0.82
Cl
0.14
0.14
0.14
0.15
0.13
0.17
0.13
0.14
0.13
0.11
0.12
0.13
0.11
0.12
总和
95.45
95.65
96.00
95.70
95.59
95.72
95.53
95.49
94.96
95.39
95.73
96.22
95.88
96.27
以22个氧原子为基准计算的阳离子数和相关参数
Si
5.79
5.77
5.76
5.76
5.81
5.77
5.73
5.73
5.77
5.77
5.78
5.75
5.81
5.77
AlⅣ
1.67
1.70
1.73
1.71
1.67
1.68
1.78
1.74
1.71
1.76
1.71
1.75
1.69
1.72
AlⅥ
0.64
0.64
0.62
0.65
0.64
0.68
0.61
0.60
0.64
0.57
0.62
0.63
0.62
0.61
Ti
0.46
0.46
0.47
0.46
0.45
0.47
0.48
0.47
0.45
0.45
0.44
0.44
0.45
0.45
Fe3+
0.68
0.64
0.64
0.70
0.64
0.69
0.66
0.67
0.67
0.62
0.66
0.64
0.64
0.67
Fe2+
1.86
1.90
1.93
1.89
1.86
1.87
1.93
1.93
1.87
1.85
1.85
1.90
1.85
1.86
Mn
0.05
0.06
0.05
0.06
0.06
0.06
0.06
0.06
0.06
0.07
0.06
0.07
0.06
0.06
Mg
2.82
2.79
2.79
2.77
2.79
2.80
2.75
2.79
2.80
2.83
2.84
2.80
2.80
2.84
Ca
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
Na
0.02
0.02
0.02
0.03
0.02
0.03
0.03
0.02
0.03
0.03
0.02
0.02
0.03
0.05
K
1.79
1.83
1.82
1.79
1.81
1.79
1.79
1.83
1.82
1.84
1.81
1.84
1.82
1.81
总和
15.78
15.81
15.83
15.82
15.75
15.84
15.82
15.82
15.80
15.79
15.79
15.84
15.77
15.84
OH*
2.62
2.66
2.61
2.66
2.60
2.61
2.58
2.66
2.69
2.62
2.66
2.70
2.65
2.63
F
0.52
0.51
0.53
0.48
0.52
0.54
0.52
0.49
0.47
0.49
0.50
0.48
0.45
0.49
Cl
0.04
0.04
0.04
0.04
0.03
0.05
0.03
0.04
0.04
0.03
0.03
0.03
0.03
0.03
AlT
2.31
2.34
2.35
2.36
2.31
2.35
2.39
2.34
2.34
2.34
2.33
2.38
2.31
2.33
Fe3+/Fe2+
0.36
0.34
0.33
0.37
0.34
0.37
0.34
0.35
0.36
0.33
0.36
0.34
0.34
0.36
Fe2+/(Mg+Fe2+)
0.40
0.41
0.41
0.40
0.40
0.40
0.41
0.41
0.40
0.40
0.40
0.40
0.40
0.40
XMg
0.60
0.59
0.59
0.60
0.60
0.60
0.59
0.59
0.60
0.60
0.60
0.60
0.60
0.60
Fe#
0.27
0.25
0.25
0.27
0.26
0.27
0.25
0.26
0.26
0.25
0.26
0.25
0.26
0.26
Mg#
0.53
0.52
0.52
0.52
0.53
0.52
0.51
0.52
0.52
0.53
0.53
0.52
0.53
0.53
MF
0.52
0.52
0.52
0.51
0.52
0.52
0.51
0.51
0.52
0.53
0.52
0.52
0.52
0.52
T/℃
746
742
746
743
743
748
747
745
742
742
741
737
742
742
P/MPa
46
56
59
62
47
59
70
57
57
55
52
67
48
53
H/km
1.74
2.12
2.21
2.33
1.78
2.24
2.66
2.17
2.16
2.09
1.95
2.54
1.82
2.01
Ⅳ(F)
0.96
0.98
0.94
1.01
0.94
0.96
0.94
0.99
1.03
0.95
0.97
0.99
1.01
0.97
Ⅳ(Cl)
-4.58
-4.56
-4.55
-4.58
-4.54
-4.66
-4.53
-4.55
-4.54
-4.48
-4.52
-4.52
-4.49
-4.52
Ⅳ(F/Cl)
5.54
5.54
5.49
5.59
5.48
5.62
5.46
5.54
5.57
5.43
5.49
5.51
5.49
5.49
log(fH2O/fHF)fluid
1.36
1.38
1.34
1.41
1.34
1.36
1.34
1.40
1.44
1.35
1.37
1.40
1.41
1.37
log(fH2O/fHCl)fluid
3.21
3.21
3.22
3.19
3.24
3.12
3.23
3.22
3.24
3.31
3.27
3.26
3.30
3.27
log(fHF/fHCl)fluid
0.65
0.63
0.68
0.58
0.70
0.56
0.69
0.62
0.60
0.76
0.70
0.65
0.69
0.70
续表1-2
Continued Table1-2
组分
29
30
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
花岗斑岩
石英二长斑岩(类型二)
SiO2
36.93
36.90
38.05
38.20
38.34
38.49
38.41
38.88
38.96
38.87
39.21
39.44
39.47
39.57
Al2O3
12.71
12.71
12.73
12.83
12.90
12.93
12.98
13.02
13.07
13.22
13.14
13.21
13.29
13.24
TiO2
3.87
3.88
2.99
2.95
3.08
3.06
3.15
3.16
3.15
3.15
3.07
3.07
3.19
3.13
FeOT
19.24
18.97
17.49
18.18
18.41
18.33
18.62
18.56
18.76
18.47
19.01
18.97
19.18
18.87
MnO
0.41
0.42
0.25
0.25
0.27
0.26
0.24
0.27
0.26
0.25
0.26
0.22
0.23
0.24
MgO
11.53
11.61
13.20
13.26
13.36
13.37
13.45
13.34
13.57
13.54
13.56
13.64
13.58
13.61
CaO
-
0.01
-
0.02
-
-
0.01
-
0.02
0.02
0.02
0.01
0.03
0.03
Na2O
0.11
0.10
0.14
0.10
0.12
0.06
0.09
0.07
0.06
0.05
0.04
0.06
0.06
0.06
K2O
9.33
9.19
9.61
9.59
9.39
8.87
8.21
8.19
7.71
7.43
7.12
6.83
6.40
6.13
F
0.72
0.81
1.38
1.44
1.56
1.50
1.59
1.56
1.60
1.60
1.64
1.63
1.63
1.54
Cl
0.13
0.13
0.21
0.25
0.20
0.22
0.22
0.21
0.21
0.21
0.24
0.23
0.22
0.23
总和
94.98
94.73
96.05
97.07
97.63
97.09
96.97
97.26
97.37
96.81
97.31
97.31
97.28
96.65
以22个氧原子为基准计算的阳离子数和相关参数
Si
5.86
5.85
5.84
5.85
5.83
5.87
5.85
5.84
5.87
5.87
5.86
5.88
5.86
5.85
AlⅣ
1.53
1.50
1.58
1.53
1.57
1.53
1.56
1.58
1.49
1.50
1.53
1.49
1.53
1.50
AlⅥ
0.78
0.82
0.74
0.79
0.75
0.79
0.76
0.76
0.82
0.82
0.79
0.83
0.78
0.82
Ti
0.35
0.34
0.35
0.35
0.36
0.36
0.35
0.36
0.34
0.34
0.36
0.35
0.35
0.34
Fe3+
0.65
0.73
0.70
0.78
0.85
0.85
0.91
0.91
1.03
1.05
1.09
1.14
0.65
0.73
Fe2+
1.60
1.60
1.65
1.55
1.51
1.49
1.44
1.41
1.35
1.32
1.29
1.21
1.60
1.60
Mn
0.03
0.03
0.03
0.03
0.03
0.03
0.03
0.03
0.03
0.03
0.03
0.03
0.03
0.03
Mg
3.18
3.19
3.16
3.17
3.16
3.12
3.14
3.14
3.14
3.13
3.09
3.11
3.18
3.19
Ca
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
Na
0.04
0.03
0.03
0.02
0.03
0.02
0.02
0.01
0.01
0.02
0.02
0.02
0.04
0.03
K
1.77
1.73
1.72
1.62
1.52
1.50
1.43
1.39
1.31
1.26
1.19
1.15
1.77
1.73
总和
15.79
15.82
15.80
15.69
15.61
15.56
15.49
15.43
15.39
15.34
15.25
15.21
15.79
15.82
OH*
2.61
2.61
2.53
2.53
2.43
2.43
2.38
2.36
2.34
2.32
2.26
2.27
2.61
2.61
F
0.82
0.85
0.86
0.84
0.85
0.83
0.82
0.81
0.84
0.81
0.79
0.75
0.82
0.85
Cl
0.05
0.06
0.05
0.06
0.06
0.05
0.05
0.05
0.06
0.06
0.06
0.06
0.05
0.06
AlT
2.31
2.32
2.32
2.32
2.32
2.32
2.31
2.34
2.32
2.32
2.33
2.32
2.31
2.32
Fe3+/Fe2+
0.41
0.45
0.42
0.50
0.56
0.57
0.63
0.65
0.76
0.80
0.84
0.94
0.41
0.45
Fe2+/(Mg+Fe2+)
0.33
0.33
0.34
0.33
0.32
0.32
0.31
0.31
0.30
0.30
0.30
0.28
0.33
0.33
XMg
0.67
0.67
0.66
0.67
0.68
0.68
0.69
0.69
0.70
0.70
0.70
0.72
0.67
0.67
Fe#
0.29
0.31
0.30
0.33
0.36
0.36
0.39
0.39
0.43
0.44
0.46
0.48
0.29
0.31
Mg#
0.59
0.58
0.57
0.58
0.57
0.57
0.57
0.57
0.57
0.57
0.56
0.57
0.59
0.58
MF
0.58
0.57
0.57
0.57
0.57
0.57
0.57
0.57
0.57
0.57
0.56
0.57
0.58
0.57
T/℃
726
722
724
728
733
733
734
737
735
737
741
745
726
722
P/MPa
47
49
49
49
50
48
48
57
49
50
52
50
47
49
H/km
1.79
1.84
1.83
1.85
1.89
1.83
1.81
2.15
1.84
1.87
1.97
1.88
1.79
1.84
Ⅳ(F)
0.75
0.74
0.69
0.70
0.66
0.66
0.64
0.64
0.62
0.62
0.60
0.63
0.75
0.74
Ⅳ(Cl)
-4.88
-4.95
-4.85
-4.93
-4.94
-4.94
-4.96
-4.97
-5.05
-5.04
-5.04
-5.09
-4.88
-4.95
Ⅳ(F/Cl)
5.63
5.69
5.54
5.63
5.60
5.60
5.60
5.60
5.68
5.66
5.64
5.72
5.63
5.69
log(fH2O/fHF)fluid
1.14
1.13
1.08
1.09
1.05
1.05
1.03
1.03
1.02
1.01
1.00
1.03
1.14
1.13
log(fH2O/fHCl)fluid
3.06
2.99
3.07
3.02
3.01
3.01
3.01
3.01
2.94
2.96
2.96
2.94
3.06
2.99
log(fHF/fHCl)fluid
0.70
0.64
0.77
0.71
0.75
0.74
0.77
0.77
0.71
0.74
0.76
0.71
0.70
0.64
续表1-3
Continued Table1-3
组分
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
石英二长斑岩(类型二)
SiO2
39.63
39.89
39.31
39.52
39.32
39.76
39.71
40.07
39.95
37.62
37.79
37.50
38.11
37.69
Al2O3
13.29
13.32
13.25
13.25
13.33
13.44
13.49
13.49
13.42
12.69
12.79
12.77
12.62
12.80
TiO2
3.12
3.12
3.17
3.15
3.18
3.09
3.27
3.27
3.19
3.38
3.15
3.18
3.11
3.14
FeOT
18.85
19.02
19.14
19.06
19.08
18.95
19.38
19.47
19.40
18.83
18.87
18.94
19.06
19.04
MnO
0.22
0.25
0.24
0.24
0.26
0.25
0.22
0.28
0.27
0.24
0.24
0.29
0.24
0.24
MgO
13.71
13.65
13.51
13.73
13.52
13.75
13.64
13.75
13.70
12.69
12.94
12.68
12.92
12.73
CaO
-
0.04
0.01
0.02
0.02
0.02
0.02
0.01
0.03
0.01
-
-
-
-
Na2O
0.04
0.05
0.04
0.07
0.06
0.03
0.07
0.06
0.02
0.12
0.05
0.11
0.11
0.05
K2O
5.97
5.73
6.29
5.71
5.67
5.35
5.17
4.99
4.70
9.66
9.31
9.63
9.54
9.63
F
1.59
1.73
1.50
1.50
1.60
1.59
1.60
1.63
1.60
1.46
1.42
1.41
1.49
1.34
Cl
0.23
0.22
0.22
0.24
0.24
0.23
0.24
0.23
0.23
0.22
0.22
0.23
0.22
0.21
总和
96.65
97.02
96.68
96.49
96.28
96.46
96.81
97.25
96.51
96.92
96.78
96.74
97.42
96.87
以22个氧原子为基准计算的阳离子数和相关参数
Si
5.88
5.90
5.86
5.87
5.86
5.88
5.86
5.88
5.88
5.81
5.81
5.80
5.84
5.80
AlⅣ
1.49
1.51
1.52
1.50
1.52
1.50
1.52
1.51
1.50
1.57
1.56
1.55
1.51
1.56
AlⅥ
0.83
0.81
0.81
0.82
0.82
0.84
0.83
0.83
0.83
0.74
0.76
0.78
0.77
0.76
Ti
0.35
0.35
0.36
0.35
0.36
0.35
0.36
0.36
0.35
0.39
0.36
0.37
0.36
0.36
Fe3+
1.14
1.15
1.11
1.21
1.19
1.23
1.26
1.29
1.32
0.67
0.74
0.72
0.73
0.70
Fe2+
1.20
1.20
1.27
1.15
1.19
1.12
1.14
1.10
1.07
1.76
1.69
1.73
1.71
1.76
Mn
0.03
0.03
0.03
0.03
0.03
0.03
0.03
0.03
0.03
0.03
0.03
0.04
0.03
0.03
Mg
3.13
3.08
3.10
3.13
3.10
3.12
3.08
3.08
3.08
3.08
3.12
3.10
3.10
3.07
Ca
0
0.01
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
Na
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.02
0.02
0.01
0.02
0.02
0.01
0.03
0.02
0.03
0.03
0.01
K
1.12
1.08
1.18
1.07
1.07
1.01
0.98
0.94
0.90
1.78
1.71
1.76
1.74
1.77
总和
15.18
15.13
15.25
15.15
15.16
15.09
15.08
15.04
14.97
15.86
15.80
15.88
15.82
15.82
OH*
2.27
2.17
2.32
2.26
2.22
2.22
2.17
2.14
2.15
2.54
2.61
2.61
2.57
2.66
F
0.77
0.80
0.73
0.73
0.77
0.75
0.75
0.75
0.72
0.85
0.82
0.85
0.86
0.79
Cl
0.06
0.05
0.06
0.06
0.06
0.06
0.06
0.06
0.06
0.06
0.06
0.06
0.06
0.05
AlT
2.32
2.32
2.33
2.32
2.34
2.34
2.35
2.33
2.33
2.31
2.32
2.33
2.28
2.32
Fe3+/Fe2+
0.96
0.96
0.88
1.05
1.00
1.10
1.11
1.18
1.24
0.38
0.44
0.42
0.43
0.40
Fe2+/(Mg+Fe2+)
0.28
0.28
0.29
0.27
0.28
0.26
0.27
0.26
0.26
0.36
0.35
0.36
0.36
0.36
XMg
0.72
0.72
0.71
0.73
0.72
0.74
0.73
0.74
0.74
0.64
0.65
0.64
0.64
0.64
Fe#
0.49
0.49
0.47
0.51
0.50
0.52
0.53
0.54
0.55
0.28
0.30
0.29
0.30
0.28
Mg#
0.57
0.57
0.56
0.57
0.57
0.57
0.56
0.56
0.56
0.56
0.56
0.56
0.56
0.56
MF
0.57
0.56
0.56
0.57
0.56
0.57
0.56
0.5
0.56
0.56
0.56
0.55
0.56
0.55
T/℃
745
744
743
749
748
748
753
754
754
732
726
726
723
722
P/MPa
51
50
52
50
56
56
58
54
52
47
49
52
37
51
H/km
1.94
1.89
1.97
1.87
2.12
2.13
2.20
2.04
1.98
1.78
1.84
1.97
1.42
1.93
Ⅳ(F)
0.61
0.56
0.65
0.64
0.60
0.60
0.59
0.57
0.58
0.71
0.74
0.74
0.71
0.77
Ⅳ(Cl)
-5.09
-5.08
-5.03
-5.12
-5.11
-5.13
-5.14
-5.15
-5.16
-4.84
-4.86
-4.88
-4.86
-4.81
Ⅳ(F/Cl)
5.70
5.64
5.69
5.76
5.71
5.74
5.72
5.72
5.74
5.56
5.60
5.62
5.58
5.58
log(fH2O/fHF)fluid
1.01
0.96
1.05
1.03
1.00
1.00
0.99
0.97
0.98
1.10
1.13
1.13
1.10
1.17
log(fH2O/fHCl)fluid
2.94
2.94
2.97
2.92
2.92
2.92
2.90
2.90
2.90
3.03
3.04
3.01
3.03
3.07
log(fHF/fHCl)fluid
0.74
0.79
0.72
0.70
0.72
0.73
0.73
0.74
0.73
0.71
0.69
0.65
0.70
0.68
注:“-”表示未检测到;氧化系数Fe#=Fe3+/(Fe2++Fe3+);镁指数Mg#=Mg/(Mg+Fe3++Fe2+);XMg=Mg/(Mg+Fe2+);MF=Mg/(Mg+Fe+Mn);比值单位为1。
表2红牛-红山铜矿床燕山晚期复式岩体中黑云母LA-ICP-MS微量元素分析结果(w(B)/10-6)
Table 2 LA-ICP-MS trace element analysis results (w(B)/10-6) of biotite in Late Yanshanian composite pluton in Hongniu-Hongshan copper deposit
组分
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
花岗斑岩(类型一)
La
0.11
-
1.56
-
0.21
0.01
0.05
11.72
0.01
0.06
0.04
Ce
0.24
0.02
4.25
-
0.33
0.03
0.45
19.74
0.02
0.06
0.01
Pr
0.02
-
0.32
-
0.04
-
0.01
1.68
-
-
-
Nd
0.17
-
1.45
0.04
0.12
-
-
6.63
-
-
-
Sm
-
-
0.23
-
-
-
-
0.62
-
-
-
Eu
0.02
-
0.08
0.03
0.01
0.01
0.03
0.37
0.02
0.02
0.02
Gd
-
-
0.48
-
-
-
-
0.46
-
-
0.04
Tb
0.01
-
0.05
-
0.03
-
-
0.09
-
-
-
Dy
0.03
-
0.36
0.02
-
-
0.08
0.46
-
-
0.03
Ho
-
-
0.10
0.01
0.02
-
0.01
0.07
-
-
-
Er
0.04
-
0.08
-
0.03
-
-
0.14
-
-
-
Tm
0.01
-
0.04
0.01
-
-
-
0.04
-
-
-
Yb
-
-
0.14
0.03
0.03
-
-
0.13
-
-
-
Lu
0.01
-
0.03
-
-
-
0.02
0.02
-
-
-
Y
0.16
-
1.67
0.21
0.52
0.03
0.20
2.22
0.01
0.02
0.01
ΣREE
0.66
0.02
9.15
0.14
0.82
0.06
0.65
42.18
0.05
0.14
0.14
Rb
1070.58
1022.59
911.13
938.30
967.49
1060.39
850.75
976.23
1046.17
1126.32
1153.69
Ba
1098.98
1487.20
407.29
1019.95
641.99
909.87
1989.37
5395.96
331.31
1311.53
503.23
Sr
2.10
2.10
4.34
3.00
4.73
9.05
18.74
5.12
5.84
2.17
2.50
U
0.06
-
0.47
0.05
1.77
0.01
0.16
0.32
0.39
0.02
0.01
Pb
1.62
0.77
0.86
1.63
0.85
1.39
1.12
1.21
0.75
0.89
0.66
Cs
27.77
21.55
27.14
17.11
36.75
42.33
22.52
13.52
40.60
21.72
47.43
Ga
49.36
50.17
53.40
48.23
64.43
46.51
61.38
50.24
70.61
59.95
54.61
Th
0.10
-
0.24
0.02
7.90
0.08
0.25
0.55
0.08
-
-
Nb
25.06
53.15
36.95
41.27
14.36
20.42
20.81
116.56
100.21
35.34
40.80
Zr
0.46
0.11
1.62
0.42
1.20
-
0.49
0.98
8.53
0.15
0.12
Ta
0.41
1.14
0.48
0.60
0.18
0.24
0.25
3.24
2.35
0.87
0.99
Hf
0.02
0.02
0.06
0.05
0.07
-
-
0.05
0.26
-
-
Li
212.95
214.00
263.71
201.08
255.35
203.97
244.21
289.44
322.27
288.62
299.64
Sc
24.47
25.61
26.37
40.77
44.03
41.45
41.67
15.76
14.01
15.04
13.12
V
328.30
305.19
281.48
315.20
347.05
305.10
322.97
176.41
229.77
179.63
161.76
Cr
301.53
324.34
322.98
261.40
301.22
247.34
283.77
112.62
37.93
95.00
67.93
Co
34.22
36.43
40.31
39.91
20.35
27.25
28.18
41.34
47.94
43.78
43.74
Ni
91.77
97.66
100.02
104.51
68.84
91.03
88.70
27.25
30.17
55.56
53.04
Cu
0.20
0.65
0.80
0.17
0.53
0.38
0.07
0.70
0.41
0.23
0.77
Zn
232.53
254.37
227.18
291.85
246.36
274.38
266.54
335.58
507.26
294.80
291.21
W
1.00
0.89
1.22
0.72
0.75
0.96
0.32
0.97
0.76
0.78
0.61
续表2
Continued Table2
组分
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
石英二长斑岩(类型二)
La
-
-
0.01
4.23
0.04
0.12
0.04
0.04
0.49
-
0.26
Ce
-
0.03
-
6.73
0.09
0.06
0.01
0.09
1.03
-
0.38
Pr
-
0.01
-
0.53
0.01
0.01
-
0.01
0.05
-
0.03
Nd
-
-
-
2.60
0.03
-
-
-
-
-
0.17
Sm
-
-
-
0.38
-
-
-
0.06
-
-
-
Eu
0.04
0.07
0.06
0.30
0.04
0.08
0.06
0.10
0.06
0.02
0.12
Gd
-
-
-
0.11
-
0.07
-
-
-
-
-
Tb
-
-
-
0.02
-
-
-
-
0.01
-
-
Dy
-
-
-
0.03
-
0.02
-
-
-
-
-
Ho
-
0.01
-
0.02
-
0.01
-
-
0.01
-
-
Er
-
-
-
0.02
-
0.01
-
-
-
-
-
Tm
-
-
0.01
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Yb
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Lu
-
-
-
-
-
0.01
-
-
-
-
-
Y
-
-
-
0.46
-
-
0.02
0.06
0.06
0.04
0.02
ΣREE
0.04
0.11
0.07
14.98
0.21
0.38
0.11
0.30
1.66
0.02
0.96
Rb
772.59
889.46
786.70
831.22
878.60
863.16
893.69
915.27
839.26
937.70
824.37
Ba
939.29
805.89
1080.36
3121.73
1377.33
2470.07
1046.68
1677.63
1661.02
1479.26
1429.08
Sr
6.40
5.07
7.30
8.47
5.33
4.74
5.04
3.47
5.50
4.48
6.75
U
-
0.01
-
1.00
0.02
0.01
0.02
0.06
0.07
0.01
0.05
Pb
1.42
0.73
1.29
1.96
0.93
2.71
1.79
1.35
1.04
1.10
1.21
Cs
15.98
17.02
14.78
14.82
21.69
12.08
18.60
17.51
14.08
24.38
17.14
Ga
39.94
45.13
46.14
47.23
45.22
45.40
47.37
44.97
49.47
46.69
53.00
Th
-
0.01
0.01
3.82
0.01
-
-
0.01
0.06
-
0.03
Nb
33.35
29.17
32.94
27.37
22.50
27.90
23.62
15.35
17.50
20.06
13.55
Zr
1.09
0.34
0.15
0.30
0.26
0.17
0.26
0.53
0.54
0.16
-
Ta
0.27
0.23
0.31
0.28
0.20
0.31
0.24
0.16
0.14
0.12
0.14
Hf
0.06
0.02
0.02
-
0.01
0.01
0.03
0.02
-
-
-
Li
239.30
250.36
241.47
266.66
231.54
234.26
225.75
220.64
205.78
267.99
260.74
Sc
37.62
31.49
35.03
19.67
12.91
12.99
12.13
12.45
10.67
23.91
6.41
V
162.31
148.36
152.40
141.54
166.17
161.59
156.61
152.40
170.20
148.68
219.60
Cr
60.60
47.77
61.79
55.68
53.81
68.32
58.96
56.30
72.37
53.05
81.68
Co
51.52
48.47
49.20
50.86
50.64
51.82
53.19
52.67
51.66
51.77
52.17
Ni
44.26
45.47
42.64
48.31
53.45
53.70
54.41
53.43
54.13
43.82
66.57
Cu
1.04
0.58
0.58
0.51
0.24
0.69
-
0.29
0.81
0.57
0.83
Zn
396.68
393.21
384.64
463.26
391.71
376.63
373.90
366.19
361.22
502.80
340.44
W
0.23
0.17
0.05
0.82
0.46
0.37
0.30
0.49
2.42
0.28
0.22
注:“-”表示低于检测限。
图6黑云母与全岩主量元素(a)、微量元素含量(b)平均大陆地壳标准化对比图(全岩数据来自周杰虎等, 2023,平均大陆地壳值据Rudnick et al., 2014)
Fig. 6 Comparison diagram of major (a) and trace element composition (b) between biotite and whole rock data (whole rock data after Zhou et al., 2023, the average composition of the continental crust after Rudnick et al., 2014)
图7红牛-红山复式岩体中黑云母Ti-Mg/(Mg+Fe)等温线图(底图据Henry et al., 2005)
Fig. 7 Diagram of Ti-Mg/(Mg+Fe) for biotites from theHongniu-Hongshan composite pluton (base map afterHenry et al., 2005)
4.2成岩指示意义大量的研究已经证明黑云母成分除了可以估算氧逸度、地质压力和地质温度以外,在某些情况下,还可以用于判断岩石成因类型及构造背景等(Abdel-Rahman, 1994;Shabani et al., 2003;Dahlquist et al., 2010;Zhang et al., 2015;叶茂等, 2017)。通过对造山和非造山岩系中黑云母成分的系统对比研究,Abdel-Rahman(1994)指出造山钙碱性岩系(I型花岗岩)中的黑云母相对富Mg;过铝质S型花岗岩中黑云母明显富Al;而非造山碱性岩系(A型花岗岩)中黑云母富Fe、成分近铁云母。在此结论的基础上,Dahlquist等(2010)研究指出,黑云母成分中的Fe2+/(Fe2++Mg)>0.8是区分A型与I、S型花岗岩的重要判别指标。此外,I型和S型花岗岩的区分还可通过岩石中黑云母氧化系数(Fe#)及镁指数(Mg#)值,S型花岗岩较I型花岗岩具有更低的Fe#和Mg#值(徐克勤,1984)。黑云母的MF指数也可分辨花岗岩种类,当MF>0.5时,为I型花岗岩,当MF<0.5时,为S型花岗岩(Yang et al., 2015)。
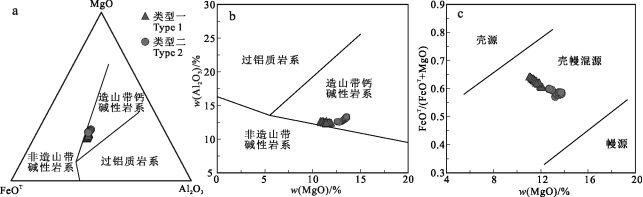
红牛-红山燕山晚期复式岩体中2种类型黑云母均表现为富镁的特征,Fe2+/(Fe2++Mg)值介于0.26~0.42之间,属于镁质黑云母,均具有较高的Fe#(0.25~0.55)和Mg#(0.51~0.59),并且MF值在0.50~0.58之间。在黑云母MgO-FeOT-Al2O3(图8a)和MgO-Al2O3(图8b)对岩石成因类型的判别图解中,2种类型黑云母成分均落入造山带钙碱性岩性范围内。这些特征指示红牛-红山燕山晚期复式岩体2种岩性均为I型花岗岩。
黑云母中元素含量尤其是Mg含量与花岗岩的形成有很大关系,MgO和FeO含量可以作为判断岩石物质来源的依据(周作侠, 1986),典型幔源黑云母中w(MgO)>15%;壳源黑云母中w(MgO)<6%。红牛-红山铜矿复式岩体中2种类型黑云母w(MgO)=11.01%~13.75%,平均值12.40%,应属于壳幔混合物质来源。在黑云母FeOT/(FeOT+MgO)-MgO图解(图8c)中,2种类型黑云母成分落于壳幔混源区域,并形成较明显的混合趋势线,反映了该复式岩体具壳幔混源的成因特征,表明母岩浆为壳幔熔体混合的产物。
图8红牛-红山复式岩体中黑云母MgO-FeOT-Al2O3图解(a,底图据Abdel-Rahman, 1994)、黑云母Al2O3-MgO图解(b,底图据Abdel-Rahman, 1994)和黑云母源区FeOT/(FeOT+MgO)-MgO判别图(c,底图据周作侠, 1986)
Fig. 8 Diagrams of MgO-FeOT-Al2O3(a, base map after Abdel-Rahman, 1994), Al2O3-MgO(b, base map after Abdel-Rahman, 1994) and FeOT/(FeOT+MgO)-MgO (c, base map after Zhou, 1986) for biotite from the Hongniu-Hongshan composite pluton
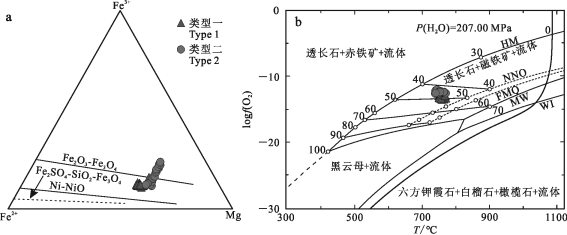
4.3成矿指示意义4.3.1岩浆氧逸度除温度和压力条件外,岩浆氧逸度与含水量对岩浆演化过程起至关重要作用。实验研究认为,与磁铁矿和钾长石共生的黑云母中Fe3+、Fe2+及Mg2+值可估算结晶氧逸度。氧逸度是影响岩浆过程的一个重要参数,对于斑岩型铜矿而言,成矿岩浆的氧逸度是一个重要的指示成矿性好坏的指标。Wones等(1965)研究发现,随着岩浆氧逸度的增加,镁铁质矿物的XMg也会增加,并且提出了一个用黑云母成分估算氧逸度的图解(Fe3+-Fe2+-Mg图解)。笔者也利用该图解估算了2种类型黑云母的氧逸度(如图9a),在Fe3+-Fe2+-Mg图解(图9a)中,2种类型黑云母样品投点落于Fe2O3-Fe3O4与Ni-NiO两条缓冲线之间及Fe2O3-Fe3O4缓冲线之上。根据Wones等(1965)提出的在P(H2O)=207.0 MPa的条件下基于黑云母稳定度[100×Fe/(Fe+Mg)]的logf(O2)-T的图解(图9b)结合黑云母Ti温度计所估算出的黑云母结晶温度,估算氧逸度logf(O2)为-14.1~-11.9,投点位于Fe2O3-Fe3O4与Ni-NiO缓冲线之间,表示其形成于高氧逸度环境中。
高氧逸度是斑岩型、浅成低温热液型Cu-Mo-Au矿床形成的重要条件之一,近些年,越来越多的研究表明,岩浆岩自身的氧逸度和温度等物化条件是决定其能否形成Cu、Au、Mo矿化的关键控制因素(Linnen et al., 1996;Mungall, 2002;Sun et al., 2015)。目前,普遍认为与Cu、Au和Mo成矿作用有关的致矿岩体具有较高的氧逸度,其氧逸度多在NNO和HM氧逸度缓冲曲线之间(Parsapoor et al., 2015)或大于FMQ+2(Mungall, 2002)。Cu、Mo作为亲硫元素,在岩浆结晶分异过程中如果S2-大量存在就会导致Cu、Mo硫化物过饱和而过早沉淀,不利于在残余岩浆中Cu、Mo的富集和晚阶段含Cu、Mo岩浆流体的形成;在高氧逸度条件下,岩浆中的S绝大多数以SO
 或SO2的形式溶解于硅酸盐熔体中,硫化物难以达到饱和,导致在岩浆演化的早期阶段不易发生硫化物的沉淀,从而使得Cu、Mo等亲硫元素在残余岩浆中逐步富集并分配进入岩浆流体相,为后续的矿化蚀变提供充足的物质来源(Sun et al., 2015)。从图9a、b可以看出,红牛-红山石英二长斑岩中黑云母的氧逸度高于花岗斑岩,在岩浆侵位过程中,较高的氧逸度导致石英二长斑岩母岩浆中硫化物溶解度高于花岗斑岩,最终在石英二长斑岩中形成了更好的Cu、Mo矿化。
或SO2的形式溶解于硅酸盐熔体中,硫化物难以达到饱和,导致在岩浆演化的早期阶段不易发生硫化物的沉淀,从而使得Cu、Mo等亲硫元素在残余岩浆中逐步富集并分配进入岩浆流体相,为后续的矿化蚀变提供充足的物质来源(Sun et al., 2015)。从图9a、b可以看出,红牛-红山石英二长斑岩中黑云母的氧逸度高于花岗斑岩,在岩浆侵位过程中,较高的氧逸度导致石英二长斑岩母岩浆中硫化物溶解度高于花岗斑岩,最终在石英二长斑岩中形成了更好的Cu、Mo矿化。
图9红牛-红山复式岩体中黑云母Fe3+-Fe2+-Mg图解(a,底图据Wones, 1965)和logf(O2)-T图解(b,底图据Wones, 1965)
Fig. 9 Diagrams of Fe3+-Fe2+-Mg (a, base map after Wones, 1965) and logf(O2)-T(b, base map after Wones, 1965) for biotite from the Hongniu-Hongshan composite pluton
4.3.2黑云母化学成分黑云母的化学成分对于矿化具有重要的指示作用,特别是对斑岩型铜矿、钨锡矿以及花岗岩型铀矿的含矿性评价(秦克章等, 2009;张龙等, 2017;周云等,2017)。秦克章等(2009)认为黑云母是斑岩铜矿及其他热液铜矿中重要的成矿指示矿物,黑云母化的强弱与铜矿化强度有直接的正相关关系。Moshefi等(2018)研究指出在斑岩型铜矿中,含矿岩体中黑云母F、Cl含量高于无矿岩体,与成矿有关的黑云母Mg/Fe比值一般大于0.5,表现富镁、低铁特征,w(TiO2)多大于3%,w(Al2O3)多小于15%,矿化黑云母w(CaO)一般小于0.5%,K/Na比值多大于10,表现高钾、低钠、钙的特点;同类非矿化岩石中的黑云母Mg/Fe比值则小于0.5,w(TiO2)小于3%,w(Al2O3)大于15%。
本次研究的2种类型黑云母Mg/Fe比值为0.99%~1.35%,均大于0.5%;w(TiO2)=2.95%~4.18%,仅有2个测试点数据小于3%,分别为2.99%和2.95%;w(Al2O3)=12.55%~13.49%,均小于15%;2种类型黑云母均具有高钾、低钠和钙的特征,w(CaO)为低于检出限至0.06%,K/Na比值为35.61~171.70。所有结果均落在有利于矿化的范围内,指示红牛-红山燕山晚期复式岩体具备一定的成矿潜力。
4.3.3黑云母挥发分
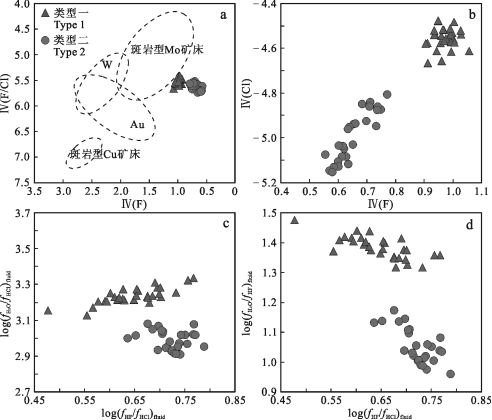
在金属元素运移过程中卤族元素发挥着重要的作用,因此,黑云母中的F、Cl含量常被用来判定岩体的矿化和非矿化程度(Munoz, 1992;唐攀等, 2017),成矿流体中卤族元素(F、Cl)的存在有利于成矿元素的运移(肖庆玲等, 2018)。斑岩型铜矿床中岩浆大多表现富Cl特征,而斑岩型钼矿床岩浆一般表现为富F(Munoz, 1984)。本文2种类型黑云母卤素地球化学计算如表1所示。2类黑云母均具有相对富F(0.64%~1.73%,平均1.15%)、贫Cl(0.11%~0.25%,平均0.18%)的特征,这与F、Cl替代OH的程度有关,由于Cl离子半径(1.81Å)大于F离子半径(1.31Å)与OH离子半径(1.38Å),导致F在OH位置上的置换量明显大于Cl(Munoz, 1984)。黑云母Mg/Fe值对卤族元素置换OH有较大影响,低Mg/Fe值黑云母富集Cl,高Mg/Fe值的黑云母则倾向于富集F(Munoz, 1984),这是由被称为“Fe-F规避”和“Mg-Cl规避”的晶体效应导致的,为了准确反映黑云母中挥发组分的富集程度,校正“Fe-F”和“Mg-Cl”规避效应的影响,本文根据Munoz(1984)提出的Ⅳ(F)和Ⅳ(Cl),即黑云母F、Cl的截距来反映其在黑云母中的相对富集程度。计算公式如下:
Ⅳ(F)=1.52Xphl+0.42Xann+0.20Xsid-log (XF/XOH)
Ⅳ(Cl)=-5.01-1.93XMg-log (XCl/XOH)
Ⅳ(F/Cl)=Ⅳ(F)-IV(Cl)
Xphl=Mg/(八面体阳离子数);Xsid=[(3-Si/Al)/1.75][1-XMg];Xann=1-XMg-Xsid,XF,XCl和XOH分别是黑云母羟基位上的F、Cl、OH的摩尔分数。
通过上述公式计算得到类型一黑云母Ⅳ(F)值为0.91~1.06,平均值0.97,Ⅳ(Cl)值为-4.67~-4.48,平均值-4.56,Ⅳ(F/Cl)值为5.43~5.68,平均值5.53;类型二黑云母Ⅳ(F)值为0.56~0.77,平均值0.65,Ⅳ(Cl)值为-5.16~-4.81,平均值-5.00,Ⅳ(F/Cl)值为5.54~5.76,平均值5.65。Ⅳ(F)值越小指示黑云母中F富集程度越高,Ⅳ(Cl)一般为负值,其绝对值越大,指示黑云母中Cl富集程度越高(Munoz,1984)。在Ⅳ(F/Cl)-Ⅳ(F)图解(图10a)中,2种类型黑云母计算结果均投于斑岩Mo矿床附近区域,由此可见红牛-红山燕山晚期复式岩体较其他斑岩型铜矿床岩体更富F,这一结论与在该复式岩体中发现辉钼矿脉及星点状辉钼矿的地质现象相一致。此外,与类型一相比,类型二黑云母更为富F、Cl(图10b),指示石英二长斑岩较花岗斑岩具有更大的成矿潜力。
如前所述,黑云母中F、Cl的含量与金属运移密切相关,对斑岩型铜钼矿床形成过程有着重要的作用。因此,黑云母中F、Cl含量常被用来计算岩浆或热液的卤素逸度作为成矿条件评估的依据(唐攀等, 2017)。Munoz(1992)基于黑云母与热液间的F-Cl-OH交换改进系数,利用黑云母成分计算与黑云母成分平衡的硅酸盐熔体和含水流体相中的卤素逸度比值log(fH2O/fHF)、log(fH2O/fHCl)和log(fHF/fCl),计算公式如下:
log(fH2O/fHF)fluid=1000/T(2.37+1.1Xphl)+0.43-
log(XF/XOH)biotite
log(fH2O/fCl)fluid=1000/T(1.15-0.55Xphl)+0.68-
log(XCl/XOH)biotite
log(fHF/fCl)fluid=-1000/T(1.22-1.65Xphl)+0.25+
log(XF/XCl)biotite
其中Xphl是黑云母八面体位置上Mg的摩尔分数,XF、XCl和XOH分别是黑云母羟基位上的F、Cl、OH的摩尔分数,T是卤素交换反应的温度(单位K)。
计算结果如表1所示,与燕山晚期花岗斑岩共存的热液流体log(fH2O/fHF)fluid值为1.31~1.47,平均值1.38;log(fH2O/fHCl)fluid值为3.12~3.33,平均值3.23;log(fHF/fHCl)fluid值为0.48~0.77,平均0.65;与燕山晚期石英二长斑岩共存的热液流体log(fH2O/fHF)fluid值为0.96~1.17,平均值1.05;log(fH2O/fHCl)fluid值为2.90~3.07,平均值2.98;log(fHF/fCl)fluid值为0.64~0.79,平均0.72。不难看出,红牛-红山燕山晚期复式岩体中类型二黑云母的log(fHF/fCl)fluid值略高于类型一,指示了与石英二长斑岩中黑云母成分平衡的硅酸盐熔体(或含水流体相)中相对富集HF,对应了更高的演化程度(郑瑜林等,2022),同时,类型二黑云母较类型一具有更低的log(fH2O/fHCl)fluid和log(fH2O/fHF)fluid值(图10c、d),指示石英二长斑岩流体中更富含HCl和HF。因此,Cu、Mo元素更趋向于在石英二长斑岩中富集,形成Cu-Mo矿化或具有经济价值的Cu-Mo矿体。
图10红牛-红山复式岩体中黑云母与挥发分相关图解
a.Ⅳ(F/Cl)-Ⅳ(F)图解(底图据Jin et al., 2018);b.Ⅳ(Cl)-Ⅳ(F)图解;c. log(fH2O/fHCl)fluid-log(fHF/fCl)fluid图解;d. log(fH2O/fHF)fluid-log(fHF/fHCl)fluid图解
Fig. 9 Correlation diagrams of biotite and volatile from the Hongniu-Hongshan composite pluton
a.Ⅳ(F/Cl)Ⅳ(F) diagram (base map after Jin et al., 2018); b.Ⅳ(Cl)-Ⅳ(F) diagram; c. log(fH2O/fHCl)fluid-log(fHF/fHCl)fluiddiagram; d. log(fH2O/fHF)fluid-log(fHF/fHCl)fluiddiagram
5结论(1)滇西北红牛-红山铜矿燕山晚期含矿复式岩体中黑云母均属于镁质黑云母,母岩浆为碰撞后造山作用背景下壳幔熔体混合的产物。
(2)黑云母结晶物理化学条件估算结果表明,红牛-红山燕山晚期复式岩体结晶温度为722~754℃;侵位深度为1.42~2.73 km,氧逸度logf(O2)为-14.1~-11.9,指示该复式岩体属于高温,浅成-超浅成相、高氧逸度岩体。
(3)根据2种类型黑云母成分特征综合分析,指示红牛-红山燕山晚期复式岩体为I型花岗岩,属于造山带钙碱性岩系。
(4)黑云母成分特征及其反映出的温度、压力、氧逸度等都指示该复式岩体具备斑岩成矿性的特点,黑云母挥发分特征指示其具有同时发生Cu、Mo矿化的潜力,并且侵位较浅的石英二长斑岩具有更大的成矿潜力。
致谢野外工作期间得到了云南黄金集团红牛矿业有限公司的大力支持。中国冶金地质总局山东局测试中心为实验研究提供了电子探针和激光剥蚀测试。在此一并表示感谢。
-
参考文献
摘要
滇西北红牛-红山斑岩-矽卡岩型大型铜矿床位于格咱铜多金属矿集区中部,其成矿作用与晚白垩世花岗质岩浆活动存在密切联系,矿区内发育燕山晚期花岗斑岩-石英二长斑岩复式岩体,矿体主要产于斑岩体以及与斑岩有关的矽卡岩中。铜钼矿化在空间上的分布具有明显的差异性,深部揭露的花岗斑岩发育弱黄铜矿化、辉钼矿化,而石英二长斑岩中发育较强的铜钼矿化,局部出现全岩矿化的特点,总体表现出浅部、接触带矿化程度高,向深部逐渐降低的趋势,导致这种差异的原因尚未明确。在详细的岩相学观察基础上,文章对复式岩体中的黑云母开展了EMPA及LA-ICP-MS原位微区分析,旨在查明矿区花岗斑岩-石英二长斑岩复式岩体形成时的物理化学条件以及导致二者含矿差异性的制约因素。结果表明,2种类型黑云母具有低Al,高Mg、Ti的特征,均属于镁质黑云母;黑云母成分显示红牛-红山燕山晚期复式岩体为具壳幔混源特征的I型花岗岩,属于高温、浅成-超浅成相、高氧逸度岩体。花岗斑岩结晶温度为737~751℃,压力为46~72 MPa,对应深度1.74~2.73 km,平均为2.17 km;石英二长斑岩结晶温度为722~754℃,压力为37~58 MPa,对应深度1.42~2.20 km,平均为1.91 km,氧逸度略高于花岗斑岩。花岗斑岩中黑云母的Ⅳ(F)值为0.91~1.06,Ⅳ(Cl)值为-4.67~-4.48,石英二长斑岩中黑云母Ⅳ(F)值为0.56~0.77,Ⅳ(Cl)值为-5.16~-4.81,与花岗斑岩共存的热液流体log(fH2O/fHF)fluid值为1.31~1.47,与石英二长斑岩共存的热液流体log(fH2O/fHF)fluid值为0.96~1.17,表明该复式岩体2种岩性均显示高F、Cl特征,石英二长斑岩流体中更富含HCl和HF。这些特征表明红牛-红山燕山晚期复式岩体具有同时发生Cu、Mo矿化的潜力,并且Cu、Mo元素更趋向于在石英二长斑岩中富集。较高的氧逸度和卤素含量可能是导致石英二长斑岩和花岗斑岩含矿差异性的主要原因。
Abstract
The Hongniu-Hongshan porphyry-skarn large-scale copper deposit in northwestern Yunnan is located in the central part of the Gezan copper polymetallic ore concentration area. The mineralization of this deposit is closely related to the Late Cretaceous granitic magmatic activity, and the Late Yanshanian granite porphyry-quartz monzonitic porphyry composite pluton is developed in the area. The ore bodies are mainly disseminated and veinlet in the porphyry and porphyry-related skarn. The spatial distribution of copper-molybdenum mineralization is obviously different. In the deep part, granite porphyry with weak chalcopyrite and molybdenite mineralization is exposed, while strong copper-molybdenum mineralization is developed in the shallow quartz monzonite porphyry. The characteristics of whole rock mineralization are generally characterized by high degree of mineralization in the shallow and contact zone, and gradually decreasing to the deep. The reasons for this difference are not yet clear. On the basis of detailed petrographic observation, Electron Microprobe Analysis (EMPA) and Laser Ablation Inductively-Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) techniques were used to investigate the major and minor element compositions of biotite in the composite rock mass, so as to identify the physicochemical conditions of the granite porphyry-quartz monzonitic porphyry composite pluton in this area and the restrictive factors leading to the difference of ore-bearing between the two rocks. The results show that the two types of biotite have the characteristics of low Al, high Mg and Ti, and both belong to magnesian biotite. The biotite composition shows that the Hongniu-Hongshan Late Yanshanian composite rock mass is an I-type granite with crust-mantle mixed source characteristics, which belongs to high temperature, shallow-ultrashallow phase and high oxygen fugacity rock mass. The crystallization temperature of granite porphyry is 737~751℃, the pressure is 46~72 MPa, corresponding to the depth of 1.74~2.73 km, with an average of 2.17 km. The crystallization temperature of quartz monzonite porphyry is 722~754℃, the pressure is 37~58 MPa, and corresponding to the depth of 1.42~2.20 km, with an average of 1.91 km, the oxygen fugacity is slightly higher than that of granite porphyry. TheⅣ(F) values of biotite in granite porphyry are 0.91~1.06, and theⅣ(Cl) values are-4.67~-4.48. TheⅣ(F) values of biotite in quartz monzonite porphyry are 0.56~0.77, and theⅣ(Cl) values are-5.16~-4.81. The log(fH2O/fHF) fluid values of hydrothermal fluid coexisting with granite porphyry are 1.31~1.47, and the log(fH2O/fHF) fluid values of hydrothermal fluid coexisting with quartz monzonite porphyry are 0.96~1.17. It shows that the two lithologies of the complex rock mass show high fluorine and chlorine characteristics, and the fluid of quartz monzonite porphyry is more rich in HCl and HF. These characteristics indicate that the Hongniu-Hongshan Late Yanshanian composite pluton has the potential for simultaneous copper and molybdenum mineralization. Moreover, copper and molybdenum elements tend to be enriched in quartz monzonite porphyry. Higher oxygen fugacity and halogen content may be the main reason for the difference in ore-bearing between quartz monzonite porphyry and granite porphyry.