-
裴荣富(2006)在探讨中国东部南岭地区的大规模成矿作用时,研究了中国东部中生代“构造圈热侵蚀”的作用。“构造圈”是Jordan(1977)根据研究鄂霍次克海壳幔结构提出的,是指位于陆内岩石圈和软流圈之间特殊的构造圈层,即为沿一定纬度局部出现的、绝大部分是由强亏损方辉橄榄岩质组成的、类似漂浮的大木筏体,是地球圈层中岩石圈板片插入软流圈中的构造活动体,主要指壳幔不谐调所体现的均衡补偿效应(地球科学大辞典)。补偿效应的具体表现为岩石圈部分拆离板片根(植)入地幔,称之为幔根(Mantle rooted)构造,并易发生热幔环流作用,这种作用被澳大利亚Macquarie大学在“大陆地球化学与成矿”研究中称之为“构造圈热侵蚀”(Oreilly, 1977),该层圈是形成大规模构造岩浆热事件,起到发动成矿作用异常的“引擎”,促使超巨量金属工业堆积,形成特大型矿床的主要圈层(裴荣富等,2002),实质上,这样的构造圈热侵蚀对成矿作用的贡献已经引起了相关构造地质学家和矿床学家的高度关注,陈国达等(1992)将中国东部中生代的地台活化也归结为构造圈热侵蚀,一些研究者将这种地质作用与深部地质作用和大规模成矿作用关联(邓晋福等,1996;1999;毛景文等,2000;邱瑞照等,2006a;2006b;曾普胜等,2020;2021),并认为与克拉通破坏有内在联系(朱日祥,2007;朱日祥等,2011;2012;2019;李三忠等,2010),这个主题对当下深地国家科技重大专项的研究和战略性关键矿产勘查仍然有重要意义。
1中国东部中生代构造圈热侵蚀地质记录:从厚的岩石圈根到薄的岩石圈中国东部中生代的岩石圈发生过极大地变化,从可以产出金刚石的大于200 km(Clifford,1966;池际尚等,1996;邓晋福等,1999;2000)的巨厚的克拉通龙骨变为现今只有60~80 km的“减薄”的岩石圈(邱瑞照等,2006a;2006b)。实际上经历了2个阶段:即燕山期巨厚岩石圈的克拉通阶段和现今的岩石圈变薄的非稳定克拉通阶段。
1.1巨厚岩石圈克拉通阶段巨厚岩石圈克拉通阶段主要以产出金伯利岩-钾镁煌斑岩-碳酸岩等幔源岩浆和面型分布的双峰式火山岩为特征(图1),岩浆活动的时代为燕山期(曾普胜等,2021)。金伯利岩-钾镁煌斑岩-碳酸岩的产出是大火成岩省的边缘标志(Ernst, 2014),而面型分布的双峰式火山岩则构成了典型的硅质大火成岩省(曾普胜等,2021;Ernst, 2014)。因此,燕山期的中国东部克拉通实质上是一个稳定的克拉通被伸展构造强烈拉伸,直至克拉通最后的龙骨部位均被拉开,才能使早期形成的含金刚石金伯利岩得以快速上涌,喷出地表,形成断续分布的金伯利岩/钾镁煌斑岩带(李佑国等,1991;李子云等,1993;池际尚等,1996;王玉峰等,2019),甚至在安徽栏杆一带还可形成含橄榄岩包体的碱性玄武岩都含金刚石(蔡逸涛等,2019)。而硅质大火成岩省中的双峰式火山岩则构成了中国东部构造圈热侵蚀导致地壳物质大面积重熔的典型标志,是中国东部中生代大规模成矿的重要能量和物质的来源。边缘环带的金伯利岩-钾镁煌斑岩-碳酸岩、面型大规模重熔的硅质大火成岩省特征简述于下。
1.1.1中国东部的金伯利岩-钾镁斑岩-碳酸岩带金伯利岩是大陆板内岩浆作用的产物。Clifford(1966)识别出,产金刚石的金伯利岩岩浆活动局限于古老克拉通(太古宙克拉通——Arton,年龄>25亿年)地区。通常全球产金刚石的金伯利岩分布于世界主要克拉通地区(如南非、西伯利亚、西非、南美、北美、澳大利亚、印度、俄罗斯北海滨阿尔汉格尔斯克、中国华北等),证明了Clifford认识的正确性,因此,厚的古老克拉通金伯利岩成为公认寻找金刚石的“Clifford法则”(Shiery et al., 2013)。当然,这类稳定的克拉通地幔可能遭受后期的硅酸盐熔体交代变薄而使金刚石含矿性变差(Carvalho et al., 2022)。
中国的金伯利岩主要集中分布在中国东部的华北。中国东部的含金刚石的金伯利岩(图1)也产在太古代克拉通之上,符合“Clifford法则”。
华北克拉通分布着9个金伯利岩群和1个钾镁煌斑岩群(图2),即蒙阴、复县(瓦房店)、铁岭、桓仁、鹤壁、涉县、柳林、应县和高阳金伯利岩群以及高阳钾镁煌斑岩群。
这9个金伯利岩岩群可分为2个金伯利岩省,即冀鲁辽金伯利岩省和鄂尔多斯金伯利岩-钾镁煌斑岩省,含金刚石的金伯利岩主要产在前者的蒙阴-瓦房店一带。无论含金刚石与否,要正确理解这些金伯利岩省的深部作用过程,都必须考虑这些金伯利岩(钾镁煌斑岩)不同主体(捕虏晶、早期岩浆岩、晚期岩浆)的时差问题,即金刚石/金伯利岩形成时代远早于金伯利岩岩浆喷发时代:
(1)金刚石早于金伯利岩:金刚石内的包裹体的测年结果表明,多数金刚石形成的年龄大大早于金刚石的寄主岩——金伯利岩,许多金刚石可形成于太古宙时期岩石圈底部,很久之后的白垩纪,才作为捕虏晶(Xenocryst)被金伯利岩岩浆携带至地表(Shiery et al.,2013;曾普胜等,2021)。类似地,金伯利岩被认为在金刚石形成时期侵位但实际测得的侵位年龄要晚得多的例子在其他地方有多处存在,如印度南部达瓦-本德尔肯德(Dharwar-Bundelkhand)克拉通的含金刚石金伯利岩长期被认为是中元古代的(~1100 Ma)(Kumar et al., 1993; Chalapathi Rao et al., 1999; Gregory et al., 2006),而新近测得的金伯利岩的年龄则与新生代德干暗色岩同时的65 Ma(Lehmann et al., 2010)。
(2)金刚石+金伯利岩早于金伯利岩岩浆喷发:中国东部金伯利岩的侵位结晶时代被认为是早古生代的(462~457 Ma)(池际尚等,1996a;张宏福等,2007;方维萱等,2002)。然而新的研究资料表明,蒙阴地区含金刚石金伯利岩带的岩脉穿切“更早”的辉绿岩脉,而这套辉绿岩脉的年龄准确地限定为白垩纪(121~117 Ma,褚志远等,2019);这种白垩纪的金刚石上升到地表的事件,在湖南理公港的白垩纪沉凝灰岩地层中的角砾岩中产出原生金刚石(杨献忠等,2019)的事实也得到印证。
造成金伯利岩时代上为早古生代或晚中生代的结果的差异,可能是由于组成金伯利岩中的3要素(捕虏晶、熔浆、流体)之间的形成时代差异导致的。中国研究者对金伯利岩的更为科学地定义(池际尚等,1996)为:金伯利岩是“处于地幔-岩浆-碳氢氧(CHO)体系中,由地幔橄榄岩物质、低熔的钾质超基性熔浆以及CHO为主要成分的流体组成的三要素固结形成的混杂岩(hybrid rock)”,三者的时代存在差异:通常,金刚石等捕虏晶的年龄远早于其寄主岩石金伯利岩(Meyer,1985;Boyd et al., 1986;邓晋福等,1989;1996)。地球深部岩浆快速上升到地表形成的一类特殊的岩石,是地球深部探测的重要窗口和获取样品的最佳途径——可以考察“多代同堂”深部地幔物质的真面目及其历史演化。
其中,金刚石和早古生代(~450 Ma)形成的金伯利岩捕虏体也是贮存在早期太古宙克拉通(Arton)之下,直到白垩纪(~120 Ma)(褚志远等,2019;杨献忠等,2019)经过“小的扰动”才将这些金伯利岩捕虏体连同金刚石一起被金伯利岩浆喷发快速地带到地表。
1.1.2双峰式火山岩构成的硅质大火成岩省中国东部燕山期大火成岩省主要包括:①东北地区的小兴安岭-张广才岭-长白山-千山岩浆带;②大兴安岭岩浆带;③华北地区的华北北缘岩浆带;④太行山岩浆带;⑤郯庐断裂金伯利岩-钾镁煌斑岩岩浆带;⑥鲁东沿海岩浆带;⑦秦岭-大别山岩浆带;⑧华南的浙闽粤岩浆带。这些岩浆带由少量的碱性玄武岩/辉绿岩带和较多的流纹岩/花岗岩带构成双峰式火山岩带(邓晋福等,2015;邢光福等,2015),多呈面型分布,不同于传统的岛弧型安山岩/闪长岩带,是大火成岩省中的硅质大火成岩省端元(Ernst, 2014)。
硅质大火成岩省是指与大火成岩省(LIPs)潜在相关的板内和大陆裂谷系统中的硅质岩浆作用,以硅质为主,非俯冲成因的大面积(>105km2)分布的岩浆省,称其为硅质大火成岩省(SLIPs)(Pankhurst et al., 1995; Bryan et al., 2000; Ernst, 2014)。硅质大火成岩省与挤压俯冲岛弧环境下形成的安山质岩浆为主,弧形分布的钙碱性系列岩浆显著不同,其双峰式火山岩的特点指示了拉张为主的构造背景,少见斑岩铜矿。
中国东部燕山期硅质大火成岩省(图1)与全球著名的硅质大火成岩省(SLIPs)(Ernst, 2014)(如美国西海岸的马德雷山(Sierra Madre)、非洲与阿拉伯半岛之间的阿法尔(Afro-Arabian,AFAR)、西非南部的伊登戴卡(Etendeka)、印度的马拉尼(Malani)、澳大利亚南部的高乐(Gawler)及东部的肯尼迪-康纳斯-奥本(Kennedy-Connors-Auburn)的大陆区的大火成岩省的情形基本一致(Bryan, 2007;Ernst et al., 2013)。其特点是,酸性或双峰式火山作用占优势,流纹岩/花岗岩特别发育,并有同期的基性岩墙、超基性岩(金伯利岩-钾镁煌斑岩-碳酸岩)发育,部分含有金刚石,与俯冲作用形成的安山岩/闪长岩等中性岩浆作用关系不密切,是大火成岩省的一部分,也是全球分布规模较大的硅质大火成岩省。这群大火成岩省,对于理解中国东部的各类构造-成矿作用十分关键。
1.2变薄岩石圈的非稳定克拉通阶段与燕山期可产出金刚石的巨厚克拉通相比,中国东部的岩石圈进入新生代产生了显著变化,变成大陆裂谷型岩石圈,形成于岩石圈伸展环境,形成了以玄武岩类占绝对优势的新生代火山岩广布于中国大陆东部的东北平原-华北平原、闽粤桂沿海、江汉平原、沿海大陆架区等地区,岩石圈厚度变薄(多在60~80 km)(邱瑞照等,2006a;2006b)。这些地区曾经在燕山期拥有可产出金刚石的稳定克拉通的龙骨,岩石圈厚度曾大于200 km(Shiery et al., 2013)。对比之下,从燕山期的龙骨克拉通稳定区变成现今的裂谷活动带,可见其岩石圈“丢失”了100 km以上,岩石圈的变化是显著的。
2中国东部中生代构造圈热侵蚀与大规模成矿2.1构造圈热侵蚀导致大规模成作用中国东部的构造圈热侵蚀与大规模成矿作用有着密切联系(裴荣富等,1999;2013)(Shiery, 2013; Ernst, 2014)。按成矿有关的岩浆岩类型不同,可以将燕山期有关的中国东部的战略矿产资源分为2种亚类,即与深源岩浆作用(金伯利岩-钾镁煌斑岩±碳酸岩)有关的战略矿产——稀贵(PGE+Au、Ag、Co)、稀土(REE)、稀有(Nb-Ta-Zr-Hf)、稀散(Li-Be-Rb-Cs)“四稀”金属;(碱性)花岗岩类有关的战略矿产——稀有金属(W-Sn-Be-Nb-Ta)、新能源矿产(Li-U-Rb-Cs)、新材料矿产(F/萤石)、大宗战略矿产(Cu)等(图3)。
与金伯利岩/钾镁煌斑岩-基性岩-碳酸盐有关的矿产多与深断裂有关,并且在2组断裂交汇处成矿显著增强。金伯利岩/钾镁煌斑岩有关的矿床主要是金刚石矿床,以郯庐断裂带两侧的辽宁瓦房店金伯利岩群(丁俊英等,2016;付海涛,2020)、山东蒙阴金伯利岩群(褚志远等,2019)以及大井头含金刚石钾镁煌斑岩(王玉峰等,2019)最为典型,金刚石达到工业品位,是中国最重要的金刚石矿床(Shiery, 2013;宋瑞祥,2013),贵州镇远马坪(东风Ⅰ号)岩管(杨光忠,2013;杨光忠等,2019)、湖南2013宁乡云影窝岩管(李子云等,1993)发现原生金刚石,构成“湘黔钾镁煌斑岩带”,其中也有金伯利岩产出(董斌等,2006);基性岩或碱性橄榄玄武岩含金刚石的例子在郯庐断裂的苏皖地区存在(蔡逸涛等,2019),碳酸岩有关的矿床则以内蒙古巴尔哲含稀土铌钽铍碱性岩矿床(Qiu et al., 2019)、山东郗山(微山)碳酸岩-碱性杂岩稀土矿床(梁雨薇等,2017)最为著名。实质上,这套与深源成因有关的岩浆作用,与金和铂族元素-铼的富集有着不同程度的关系,山东郗山碱性杂岩中的黄铁矿富集铂族元素等(曾普胜等,2020)、归来庄基性岩脉中不仅富金,还含极高的碲(Te)(于学峰等,2010),均有幔源流体的属性。这些矿产都是幔源岩浆上侵带来的以幔源物质为主的成矿作用,是构造圈热侵蚀的结果。
2.2中国东部的成岩成矿时代均为燕山期(1)成岩时代为燕山期。蒙阴地区含金刚石金伯利岩带的岩脉切穿了“更早”的辉绿岩脉,而这套辉绿岩脉的年龄准确地限定为白垩纪(121~117 Ma,褚志远等,2019),证明这些含金刚石的金伯利岩脉不会早于白垩纪;类似地,扬子湘黔钾镁煌斑岩带的年龄也被限定在白垩纪,宁乡云影窝含金刚石的钾镁煌斑岩岩管的年龄为白垩纪((101.6±5.1)Ma,林玮鹏等,2011),与湖南常德理公港的含原地金刚石的凝灰质角砾岩地层为白垩纪(杨献忠等,2019)在时代上吻合较好。这表明,无论华北地台还是扬子地台,与金刚石有关的这类深源岩浆岩,先形成的捕虏晶矿物(如金云母、钙钛矿等)年龄均为加里东期,而更晚的爆发期或侵入期锆石年龄则为燕山晚期(早白垩世),并且可从同层位的含金刚石地层(如理公港地区含金刚石凝灰质角砾岩)得到验证,表明早白垩世是金刚石形成关键时期,与南非地区的含金刚石金伯利岩的时代(~120 Ma,Larson et al., 1996;王登红,1998)一致。也与中国金刚石地质勘查的野外观察到含金刚石金伯利岩脉和辉绿岩脉穿切侏罗系和下白垩统的事实吻合,这些被含金刚石金伯利岩脉穿切的辉绿岩脉的同位素年龄均在134~115 Ma之间(《金刚石普查与勘探》编写组,1978),与褚志远等(2019)在山东蒙阴金刚石矿带坡里矿段被含矿金伯利岩脉穿切的辉绿岩脉中测得的121 ~117 Ma的锆石U-Pb年龄一致。因此,中国东部含金刚石金伯利岩的侵位年龄为燕山期确信无疑。
含高压矿物金伯利岩脉被误认为加里东期的原因分析:英国的德比尔斯公司(De Beers Group)的Dobbs等(1991)用蒙阴金伯利岩中的高压矿物钙钛矿获得(456±8)Ma的U-Pb年龄后,中国东部的(金刚石)金伯利岩就被引导为早古生代(加里东期)的了,之后陆续有研究者获得该区金伯利岩/钾镁煌斑岩的早古生代年龄,如辽宁复县(瓦房店)金伯利岩的金云母的Rb-Sr等时线年龄(461.7±4.8)Ma(Lu et al., 1998)、山东蒙阴和辽宁瓦房店金伯利岩侵位年龄为Sm-Nd等时线(465±2)Ma(张宏福等,2007)等。实际上,这些深部形成的先成矿物或捕虏晶,无论测年精度有多高,所获得的年龄始终是捕虏晶本身的形成时间,通常远早于金伯利岩浆侵位至地表的时间。这些捕虏晶就如同在火车站提前买到车票的旅客,尽管购票时间各有不同,但它们都在等待着被金伯利岩浆带至地表的那一刻,而这一等待的时间长短也因晶而异。测定先成矿物或捕虏晶,包括钙钛矿、镁铝榴石、金刚石中的各种包体矿物,如角闪石、辉石,甚至瓦兹利石、布里奇曼石等橄榄石的高压变种,所测的年龄都常常早于幔源的金伯利岩浆快速上升到地表的时代,这就是中国东部金伯利岩带被长期被误认为是加里东期的原因。
(2)成矿时代也为燕山期。中国东部与燕山期岩浆活动有关的约60个矿床的成矿年龄统计结果(图4)显示,中国东部燕山期构造圈热侵蚀导致的大规模岩浆作用和成矿作用的峰期有两期:
第一峰期为139 Ma,辽宁瓦房店金伯利岩带内50号岩管的年龄与这一峰期接近(丁俊英等,2016);第二峰期为121 Ma,山东蒙阴含金刚石金伯利岩的侵位时期与此相当(褚志远等,2019),胶东金矿带的大规模成矿作用也属于这个时期。燕山期碳酸岩-碱性杂岩有关的稀土矿床显示出成矿时代由东北向西南逐渐变新的趋势:内蒙古巴尔哲稀土矿床(~127 Ma,Qiu et al., 2019)→山东郗山稀土矿(~121 Ma,梁雨薇等,2017)→右江盆地水银洞隐爆角砾岩型碳酸岩稀土矿床等(121~106 Ma,Ge et al., 2022)。
3讨论3.1中国东部燕山期巨厚岩石圈减薄的可能原因前人将中国东部燕山期的岩浆作用归结为平板俯冲,从中国东部沿海到内陆的长沙一带,俯冲距离在1300 km以上(图5)(李正祥等,1996;李武显等,1999;2001; Li et al., 2007)。然而,从地球动力学角度来看,1300 km以上的平板俯冲条件太苛刻:是什么力量托举着如此巨大的板片保持水平?又是什么力量能将如此长的板片向西推挤而不受阻挡?并且在整个扬子范围内均保持这样的规模和式样,这个统一指挥的同一步调的神奇力量从何而来?世界上有如此规模的平板俯冲案例可供遵循吗?这些问题都不可能从动力学机制上或计算机模型模拟得到满意的答案。
根据野外观察并参考前人(Davis, 2011a;2011b;Davis et al., 2010;2013)对华北克拉通的研究结果,中国东部厚的岩石圈(>200 km,池际尚等,1996)减薄到现金薄的(60~80 km,邱瑞照等,2006a;2006b)是青藏高原的向东推挤(Davis et al., 2010;Davis, 2011a),使白垩纪可产金刚石的巨厚岩石圈向东迁移,变形减薄所致。这种向东推挤的迁移减薄,只是青藏高原推挤作用下的岩石圈内的空间调整,而不是平板俯冲(Li et al., 2007)或者中国东部的岩石圈拆沉(Zhang et al., 2021;何梅兴等,2023)。
3.2新生代构造对华北克拉通的进一步破坏中国东部进入新生代后,存在着北东向与北西向2组共轭的张性构造带,形成中国裂谷系(刘嘉麒,1987;马杏垣等,1990)。汾渭地堑-大同-张家口裂谷火山岩带、长白山-镜泊湖火山岩带构成北东向火山岩带;江汉盆地内火山岩带、张家口-蓬莱火山岩带等则构成北西向火山岩带代表。这2组火山岩带中,都夹有来自地幔的橄榄岩包体(袁万明等,1993;储雪蕾等,1999;李延河等,2001;白志达等,2006)。实质上,闽粤桂沿海、江汉平原、沿海大陆架区等地区均存在新生代裂谷型火山活动,构成中国东部北东向为主,兼有北西向分布的裂谷火山岩带(Li et al., 2010;刘嘉琪等,2015),岩石圈厚度大大减薄至60~80 km。这组共轭张性构造带或中国裂谷系的形成正是在太平洋构造域北东方向牵拉的构造背景下,青藏高原之下的地幔流(莫宣学等,2004)在北东方向沿古老的裂谷带(软弱带)上涌,到浅表部位分散到郯庐断裂带、汾渭地堑喷出的结果。北东向的汾渭-大同火山岩带和长白山火山岩带与北西向的张家口-蓬莱大断裂控制的火山岩带(包括含蓝宝石昌乐方山玄武岩带)和江汉盆地玄武岩带等,构成了中国裂谷系内重要的新生代岩浆活动带和战略性矿产(如富钾锂卤水、油气等)集中区。
4结论(1)中国东部燕山期经历的强烈的构造圈热侵蚀,表现为幔源的金伯利岩±钾镁煌斑岩±碳酸岩岩浆带,伴随有双峰式火山岩组合为主的面型岩浆岩带组成的硅质大火成岩省。
(2)燕山期构造圈热侵蚀伴随大规模成矿作用,形成稀土-稀有-稀散-稀贵、金刚石、铀矿、油气-氢等组成的战略性矿产沿深断裂带依次分布。
(3)燕山期构造圈热侵蚀导致的成岩成矿时期在150~100 Ma,其中有2个峰期为主要成岩成矿期,分别为139 Ma和121 Ma。
(4)从燕山期具有大于200 km的巨厚龙骨的稳定克拉通变为现今仅有60~80 km岩石圈的主要原因是新生代青藏高原的岩石圈向东推挤导致岩石圈向东迁移变形,而不是平板俯冲或拆沉所致。
致谢值导师裴荣富院士101华诞之际,能将裴先生早期提出的“中国东部构造圈热侵蚀”思想做一些补充思考,也算是对先生的学术思想的传承。裴先生一生耕耘学术,蜚声海内外,尤其对构造与成矿的大构架的思考,形成了一系列独特的找矿思维和理论,是永远值得我们去仔细品味和长期实践的。
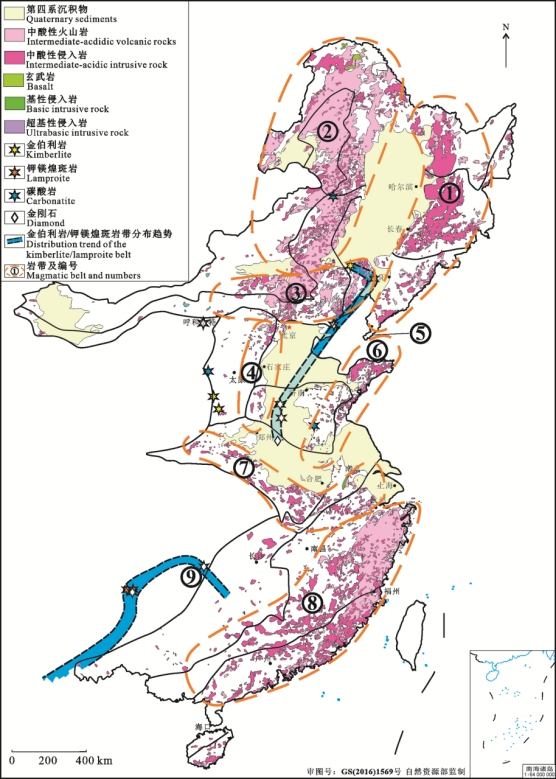
图1中国东部燕山期大火成岩省岩浆岩分布图(侵入岩据邓晋福等,2015;喷出岩据邢光福等,2015;金伯利岩-钾镁煌斑岩-金刚石据宋瑞祥,2013;大火成岩省据曾普胜等,2021改编)
Fig. 1 Distribution map of magmatic rocks of the Yanshanian large igneous province in eastern China (intrusions after Deng et al., 2015; extrusions after Xing et al., 2015;kimberlites-lamproites-diamonds after Song, 2013;large igneous province modified after Zeng et al., 2021)
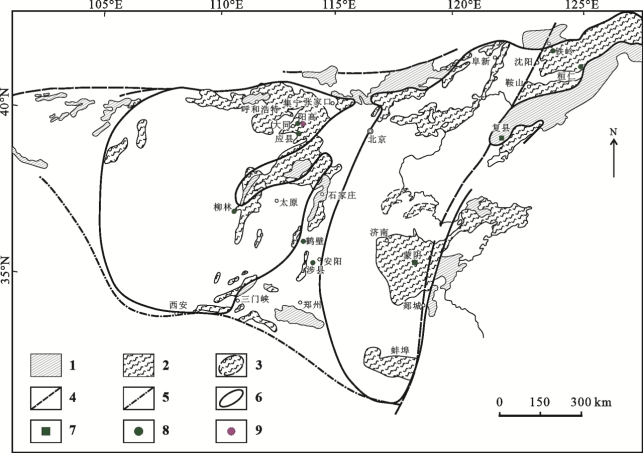
图2华北地台太古宙—古元古代基底岩石与金伯利岩分布略图(据马杏垣等,1983;邓晋福等,1996资料改编) 1—元古宇基底(Proton);2—太古宇结晶基底(Arton);3—隐伏太古宇结晶基底;4—深大断裂;5—地台边界;6—古陆核边界;7—含金刚石金伯利岩;8—不含金刚石金伯利岩;9—钾镁煌斑岩
Fig.2 Distribution of Archean—Paleoproterozoic basements and kimberlites in North China Craton(modified after Ma et al., 1983; Deng et al., 1996) 1—Proterozoic basement (Proton); 2—Archean Crystalline Basement (Arton); 3—Concealled Archean crystalline basement; 4—Deep and large fault; 5—Platform boundary; 6—Paleo-Continental nuclei boundary; 7—Diamond-bearing kimberlite; 8—Diamond-free kimberlite;9—Lamproite
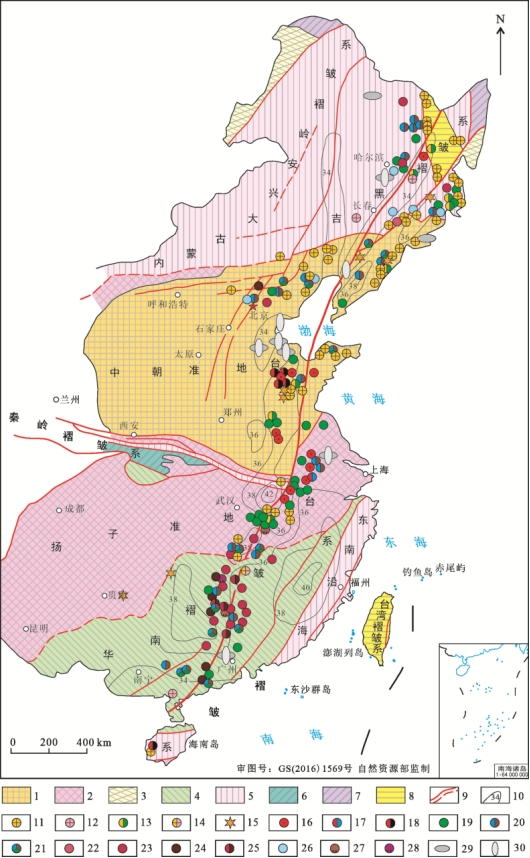
图3郯庐断裂两侧矿产分布略图(据郭文魁等,1982;赫英等,2002;曾普胜等,2020综合编制) 1—中朝准地台;2—扬子褶皱及后扬子地台盖层;3—兴凯褶皱及后兴凯地台盖层;4—加里东褶皱及后加里东地台盖层;5—海西褶皱及后海西地台盖层;6—印支褶皱及后印支地台盖层;7—燕山褶皱;8—喜马拉雅褶皱;9—深断裂及推测深断裂;10—莫霍界面视等深线;矿产资源与油气:11—金矿;12—银矿;13—金铜矿;14—金银矿;15—金刚石矿;16—铁矿;17—铁钒钛矿;18—铁钴矿;19—铜矿;20—铅锌矿;21—铜铅锌矿;22—镍矿;23—钨矿;24—锡矿;25—钨锡矿;26—钼矿;27—锑矿;28—汞矿;29—二氧化碳气藏/二氧化碳气苗;30—幔源氦气藏/氦异常
Fig.3 Simplified map showing the distribution of mineral resources of the Tan-Lu fault belt(compiled from Guo et al., 1982; He et al., 2002; Zeng et al., 2020) 1—Sino-Korean paraplatform; 2—Yangtze fold and post-Yangtze platform covers; 3—Xingkai fold and post-Xingkaian platform covers; 4—Caledonian fold and post-Caledonian platform covers; 5—Hercynian fold and post-Hercynian platform covers; 6—Indosinian fold and post-Indosinian platform covers; 7—Yanshanian fold; 8—Himalayan fold; 9—Deep fault and inferred deep fault; 10—Moho interface isobaths; Minerals and oil-gas deposits: 11—Gold deposit; 12—Silver deposit; 13—Gold-copper deposit; 14—Gold-silver deposit; 15—Diamond deposit; 16—Iron deposit; 17—Iron-vanadium-titanium deposit; 18—Iron-cobalt deposit; 19—Copper deposit; 20—Lead-zinc deposit; 21—Copper-lead-zinc deposit; 22—Nickel deposit; 23—Tungsten deposit; 24—Tin deposit; 25—Tungsten-tin deposit; 26—Molybdenum deposit; 27—Antimony deposit; 28—Mercury deposit; 29—CO2 gas reservoir/seedling; 30—Mantle-derived helium gas reservoir/helium anomaly
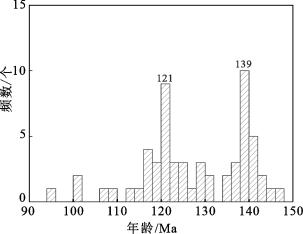
图4燕山期岩浆活动与成矿事件年龄统计直方图(据曾普胜等,2021)
Fig.4 Statistical histogram of age of magmatic activity and ore-forming event in Yanshanian(after Zeng et al., 2021)

图5燕山期华南褶皱造山带的古地理演化示意图(据Li et al., 2007;现今的地理经纬网仅作为参考) a~c.造山带向陆内迁移过程;d, e.造山带后侧拗陷盆地发育过程;f.为俯冲板片拆沉及俯冲弧重置引发的造山后岩浆作用
Fig. 5 Paleogeographic evolution of South China fold orogenic belt during Yanshanian stage (after Li et al., 2007; The current geographic grid of latitude and longitude is only for reference) a~c. Intracontinental migration process of orogenic belt; d, e. The development process of the retroorogen depression basin ; f. Post-orogenic magmatism caused by subduction plate removal and subduction arc resetting
-
参考文献
摘要
中国东部燕山期为稳定的克拉通,可以产出含金刚石的地幔来源的金伯利岩/钾镁煌斑岩/碳酸岩等,其岩石圈厚度大于200 km,并伴有大规模成矿作用,形成高压条件下才能形成的金刚石矿床沿郯庐断裂带等深断裂带产出,并有金-铁-稀土-钨锡钼铋-铜铅锌银-汞(铊)锑砷-铷铯铍铌钽矿等大宗矿产或战略性关键矿产,并在深断裂带外侧盆地中形成铀-油气-锂钾溴碘的新能源矿产和非常规油气能源矿产。成矿作用按时代分为139 Ma和121 Ma,成矿峰期显示出幕式脉动性。这种具龙骨式的稳定地台向薄的非稳定地块演变,产生“构造圈热侵蚀”的最可能原因是新生代青藏高原的挤出效应,使东亚克拉通岩石圈向东滑移,从而使原本厚的岩石圈变形减薄,同时使先前较陡的俯冲板片变得平缓,已经变薄的中国东部岩石圈在新生代又经历了太平洋构造域北东向构造的牵拉,岩石圈进一步变薄,甚至沿张家口-蓬莱深断裂分开,形成渤海湾式的北西向构造与鸭绿江式的北东向构造共轭伸展,并伴有各类幔源岩浆作用和关键矿产(稀土-蓝宝石-金-油气-氢-氦等)。因此,中国东部是深地探测和研究的理想场所,并具有战略性矿产巨大发现潜力。
Abstract
The Yanshanian eastern China is a stable craton, which can produce diamond-bearing mantle derived kimberlites/lamproites/carbonates, etc. Its lithospheric thichness is larger than 200 km and accompanied by large-scale mineralization. The diamond deposits formed under high pressure were produced along the Tanlu deep fault zone and other deep faults; while the deposits of gold/ iron/rare earth/tungsten, tin, molybdenum, bismuth/copper, lead, zinc, silver/mercury(thallium), antimony, arsenic/rubidium, cesium, beryllium, niobium, tantalum and other strategic key minerals occurred in the outer sides of diamond deposits; and in the outermost of the deep fault zone, new energy minerals and unconventional oil and gas energy minerals including uranium/oil and gas/ lithium potassium bromine iodine. The mineralization is divided into two main stages, peak ages are 139 Ma and 121 Ma, showing episodic pulsation. The most likely reason for the evolution of this keel-like stable platform attenuating as the unstable block, resulting “tectonospheric thermal erosion”, is the extrusion effect of the Tibetan Plateau in the Cenozoic, which makes the East Asian craton lithosphere slip eastward, thus thinning the originally thick lithosphere and flattening the previously steeper subduction slab. The lithosphere in eastern China, which had already been thinned, was further thinned and even separated along the Zhangjiakou-Penglai deep fault during the Cenozoic, forming the northwest structure of the Bohai Bay type and the northeast structure of the Yalujiang type. It is accompanied by various mantle-derived magmatism and key minerals(rare earth-sapphire-gold-oil-gas-hydrogen-helium, etc.). Therefore, eastern China is an ideal place for deep exploration and research, and has great potential for strategic mineral discovery.
